
Way back in 2013 our malware analysts spotted the first malicious samples related to the Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Rakhni family. That was the starting point for this long-lived Trojan family, which is still functioning to this day. During that time the malware writers have changed:
- the way their Trojans get keys (from locally generated to received from the C&C);
- the algorithms used (from using only a symmetric algorithm, through a commonly used scheme of symmetric + asymmetric, to 18 symmetric algorithms used simultaneously);
- the crypto-libraries (LockBox, AESLib, DCPcrypt);
- the distribution method (from spam to remote execution).
Now the criminals have decided to add a new feature to their creation – a mining capability. In this article we describe a downloader that decides how to infect the victim: with a cryptor or with a miner.
Distribution
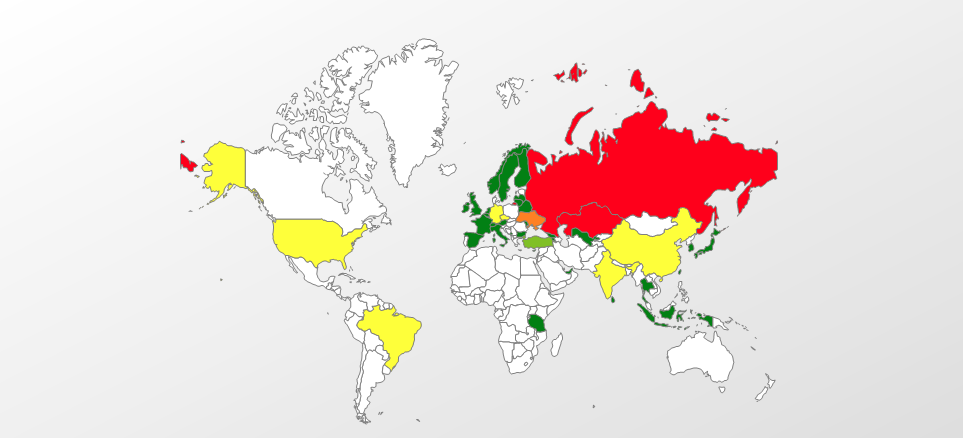
Geography of attacks
Top five countries attacked by Trojan-Downloader.Win32.Rakhni (ranked by percentage of users attacked):
| Country | %* | |
| 1 | Russian Federation | 95.57% |
| 2 | Kazakhstan | 1.36% |
| 3 | Ukraine | 0.57% |
| 4 | Germany | 0.49% |
| 5 | India | 0.41% |
* Percentage of unique users attacked in each country by Trojan-Downloader.Win32.Rakhni, relative to all users attacked by this malware
Infection vector
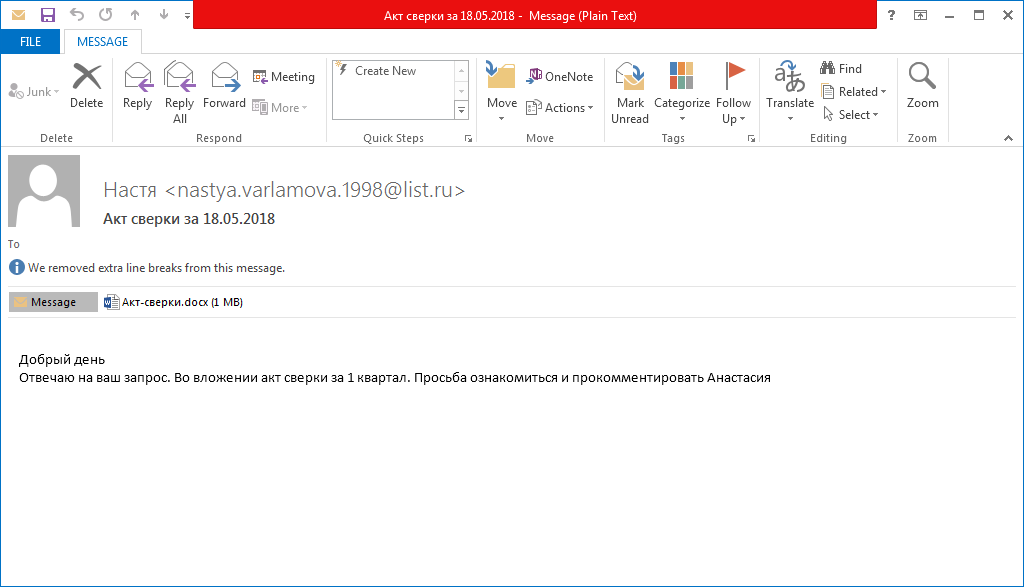
As far as we know, spam campaigns are still the main way of distributing this malware.
After opening the email attachment, the victim is prompted to save the document and enable editing.
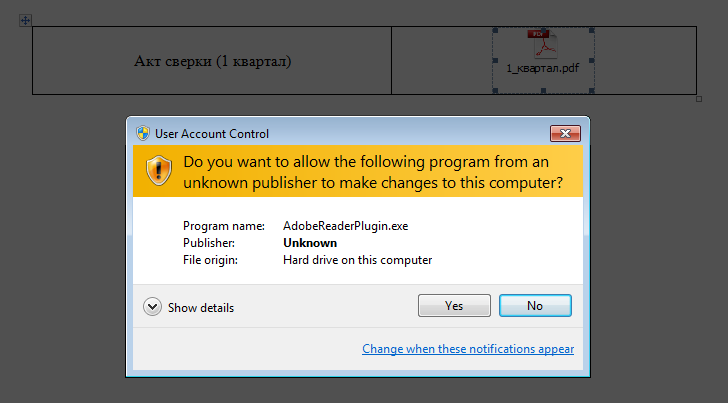
The victim is expected to double-click on the embedded PDF file. But instead of opening a PDF the victim launches a malicious executable.
Downloader
General information
The downloader is an executable file written in Delphi. To complicate analysis, all strings inside the malware are encrypted with a simple substitution cipher.
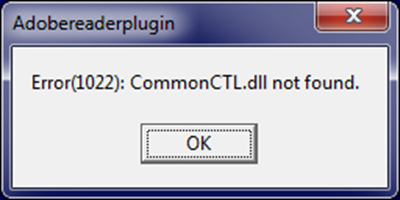
After execution, the downloader displays a message box with an error text. The purpose of this message is to explain to the victim why no PDF file opened.
To hide the presence of the malicious software in the system the malware developer made their creation look like the products of Adobe Systems. This is reflected in the icon, the name of the executable file and the fake digital signature that uses the name Adobe Systems Incorporated. In addition, before installing the payload the downloader sends an HTTP request to the address www.adobe.com.
Environment checks
After the message box is closed the malware performs a number of checks on the infected machine:
- Self path check
- The name should contain the substring AdobeReader
- The path should contain one of the following substrings:
- \TEMP
- \TMP
- \STARTUP
- \CONTENT.IE
- Registry check
Checks that in the registry there is no value HKCU\Software\Adobe\DAVersion and, if so, the malware creates the value HKCU\Software\Adobe\DAVersion = True and continues its work
- Running processes check
- Checks that the count of running processes is greater than 26
- Checks that none of the processes listed in the table below are present.
| alive.exe | filewatcherservice.exe | ngvmsvc.exe | sandboxierpcss.exe |
| analyzer.exe | fortitracer.exe | nsverctl.exe | sbiectrl.exe |
| angar2.exe | goatcasper.exe | ollydbg.exe | sbiesvc.exe |
| apimonitor.exe | GoatClientApp.exe | peid.exe | scanhost.exe |
| apispy.exe | hiew32.exe | perl.exe | scktool.exe |
| apispy32.exe | hookanaapp.exe | petools.exe | sdclt.exe |
| asura.exe | hookexplorer.exe | pexplorer.exe | sftdcc.exe |
| autorepgui.exe | httplog.exe | ping.exe | shutdownmon.exe |
| autoruns.exe | icesword.exe | pr0c3xp.exe | sniffhit.exe |
| autorunsc.exe | iclicker-release.exe.exe | prince.exe | snoop.exe |
| autoscreenshotter.exe | idag.exe | procanalyzer.exe | spkrmon.exe |
| avctestsuite.exe | idag64.exe | processhacker.exe | sysanalyzer.exe |
| avz.exe | idaq.exe | processmemdump.exe | syser.exe |
| behaviordumper.exe | immunitydebugger.exe | procexp.exe | systemexplorer.exe |
| bindiff.exe | importrec.exe | procexp64.exe | systemexplorerservice.exe |
| BTPTrayIcon.exe | imul.exe | procmon.exe | sython.exe |
| capturebat.exe | Infoclient.exe | procmon64.exe | taskmgr.exe |
| cdb.exe | installrite.exe | python.exe | taslogin.exe |
| cff explorer.exe | ipfs.exe | pythonw.exe | tcpdump.exe |
| clicksharelauncher.exe | iprosetmonitor.exe | qq.exe | tcpview.exe |
| closepopup.exe | iragent.exe | qqffo.exe | timeout.exe |
| commview.exe | iris.exe | qqprotect.exe | totalcmd.exe |
| cports.exe | joeboxcontrol.exe | qqsg.exe | trojdie.kvp |
| crossfire.exe | joeboxserver.exe | raptorclient.exe | txplatform.exe |
| dnf.exe | lamer.exe | regmon.exe | virus.exe |
| dsniff.exe | LogHTTP.exe | regshot.exe | vx.exe |
| dumpcap.exe | lordpe.exe | RepMgr64.exe | winalysis.exe |
| emul.exe | malmon.exe | RepUtils32.exe | winapioverride32.exe |
| ethereal.exe | mbarun.exe | RepUx.exe | windbg.exe |
| ettercap.exe | mdpmon.exe | runsample.exe | windump.exe |
| fakehttpserver.exe | mmr.exe | samp1e.exe | winspy.exe |
| fakeserver.exe | mmr.exe | sample.exe | wireshark.exe |
| Fiddler.exe | multipot.exe | sandboxiecrypto.exe | xxx.exe |
| filemon.exe | netsniffer.exe | sandboxiedcomlaunch.exe | ZID Updater File Writer Service.exe |
- Computer name check
- The name of the computer shouldn’t contain any of the following substrings:
- -MALTEST
- AHNLAB
- WILBERT-
- FIREEYES-
- CUCKOO
- RSWT-
- FORTINET-
- GITSTEST
- Calculates an MD5 digest of the computer name in lower case and compares it with a hundred denylisted values
- The name of the computer shouldn’t contain any of the following substrings:
- IP address check
Obtains the external IP address of the machine and compares it with hardcoded values.
- Virtual machine check
- Checks that the following registry keys don’t exist:
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\Oracle VM VirtualBox Guest Additions
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Oracle\VirtualBox Guest Additions
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\Sandboxie
- HKLM\SYSTEM\ControlSet002\Enum\VMBUS
- HKLM\HARDWARE\ACPI\DSDT\VBOX
- HKLM\HARDWARE\ACPI\DSDT\VirtualBox
- HKLM\HARDWARE\ACPI\DSDT\Parallels Workstation
- HKLM\HARDWARE\ACPI\DSDT\PRLS
- HKLM\HARDWARE\ACPI\DSDT\Virtual PC
- HKLM\HARDWARE\ACPI\SDT\AMIBI
- HKLM\HARDWARE\ACPI\DSDT\VMware Workstation
- HKLM\HARDWARE\ACPI\DSDT\PTLTD
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\SandboxieAutoExec
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Classes\Folder\shell\sandbox
- Checks that the following registry values don’t exist:
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows NT\CurrentVersion\OpenGLDrivers\VBoxOGL\Dll=VBoxOGL.dll
- HKLM\\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Disk\Enum\0=Virtual
- HKLM\\SYSTEM\ControlSet001\Control\SystemInformation\SystemProductName=VirtualBox
- Checks that none of the processes listed in the table below are present.
- Checks that the following registry keys don’t exist:
| prlcc.exe | VGAuthService.exe | vmsrvc.exe | vmware-tray.exe |
| prltools.exe | vmacthlp.exe | vmtoolsd.exe | vmware-usbarbitrator.exe |
| SharedIntApp.exe | vmicsvc.exe | vmusrvc.exe | vmware-usbarbitrator64.exe |
| TPAutoConnect.exe | vmnat.exe | vmware-authd.exe | vmwaretray.exe |
| TPAutoConnSvc.exe | vmnetdhcp.exe | vmware-converter-a.exe | vmwareuser.exe |
| VBoxService.exe | vmount2.exe | vmware-converter.exe | xenservice.exe |
| VBoxTray.exe | VMRemoteGuest.exe | vmware-hostd.exe |
If at least one of the performed checks fails, the downloader ends the process.
Installation of certificates
The downloader installs a root certificate that’s stored in its resources. All downloaded malicious executables are signed with this certificate. We have found fake certificates that claim to have been issued by Microsoft Corporation and Adobe Systems Incorporated.
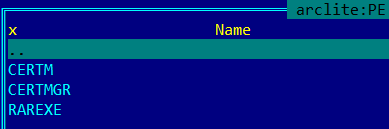
Certificates are installed using the standard utility CertMgr.exe that’s also stored in the downloader’s resources.
Before installing the certificate, the downloader drops the necessary files from the resources to the %TEMP% directory.
It then executes the following command:
CertMgr.exe -add -c 179mqn7h0c.cer -s -r localMachine root
The main decision
The decision to download the cryptor or the miner depends on the presence of the folder %AppData%\Bitcoin. If the folder exists, the downloader decides to download the cryptor. If the folder doesn’t exist and the machine has more than two logical processors, the miner will be downloaded. If there’s no folder and just one logical processor, the downloader jumps to its worm component, which is described below in the corresponding part of the article.
Cryptor decision
The Trojan downloads a password-protected archive that contains a cryptor module. The archive will be downloaded to the startup directory (C:\Documents and Settings\username\Start Menu\Programs\Startup) and then the downloader will unpack it using the command line WinRAR tool. The cryptor executable will have the name taskhost.exe.
After execution, the cryptor performs an environment check like the installer; in addition, it will check that it’s running after the downloader decision (by checking the registry value HKCU\Software\Adobe\DAVersion is present).
Interestingly, the cryptor only starts working if the system has been idle for at least two minutes. Before encrypting files, the cryptor terminates the following processes:
| 1cv7s.exe | Foxit Advanced PDF Editor.exe | mspaint.exe | soffice.exe |
| 1cv8.exe | Foxit Phantom.exe | mysqld.exe | sqlservr.exe |
| 1cv8c.exe | Foxit PhantomPDF.exe | NitroPDF.exe | sqlwriter.exe |
| 7zFM.exe | Foxit Reader.exe | notepad.exe | STDUViewerApp.exe |
| acad.exe | FoxitPhantom.exe | OUTLOOK.EXE | SumatraPDF.exe |
| Account.EXE | FoxitReader.exe | PDFMaster.exe | thebat.exe |
| Acrobat.exe | FreePDFReader.exe | PDFXCview.exe | thebat32.exe |
| AcroRd32.exe | gimp-2.8.exe | PDFXEdit.exe | thunderbird.exe |
| architect.exe | GSmeta.exe | pgctl.exe | ThunderbirdPortable.exe |
| bricscad.exe | HamsterPDFReader.exe | Photoshop.exe | VISIO.EXE |
| Bridge.exe | Illustrator.exe | Picasa3.exe | WebMoney.exe |
| CorelDRW.exe | InDesign.exe | PicasaPhotoViewer.exe | WinDjView.exe |
| CorelPP.exe | iview32.exe | postgres.exe | WinRAR.exe |
| EXCEL.EXE | KeePass.exe | POWERPNT.EXE | WINWORD.EXE |
| fbguard.exe | Magnat2.exe | RdrCEF.exe | wlmail.exe |
| fbserver.exe | MSACCESS.EXE | SmWiz.exe | wordpad.exe |
| FineExec.exe | msimn.exe | soffice.bin | xnview.exe |
In addition, if there is no avp.exe process running, the cryptor removes volume shadow copies.
The cryptor encrypts files with the following extensions:
After encryption the file extension will be changed to .neitrino.
Files are encrypted using an RSA-1024 encryption algorithm. The information necessary to decrypt the files is sent to the attacker by email.
In each encrypted directory, the cryptor creates a MESSAGE.txt file with the following contents:
Miner decision
The downloading process of the miner is the same except for the downloading folder – the miner is saved to the path %AppData%\KB<8_random_chars>, where <8_random_chars>, as the name suggests, is a string constructed from alphanumeric characters [0-9a-z].
After downloading and unpacking the archive with the miner, the Trojan does the following:
- Firstly, it generates a VBS script that will be launched after an OS reboot. The script has the name Check_Updates.vbs. This script contains two commands for mining:
- the first command will start a process to mine the cryptocurrency Monero;
- the second command will start a process to mine the cryptocurrency Monero Original. The name of the subfolder where the executable should be located (cuda) may indicate that this executable will use the GPU power for mining.
- Then, if there is a file named %AppData%\KB<8_random_chars>\svchost.exe, the Trojan executes it to mine the cryptocurrency Dashcoin.
When this analysis was carried out, the downloader was receiving an archive with a miner that didn’t use the GPU. The attacker uses the console version of the MinerGate utility for mining.
In order to disguise the miner as a trusted process, the attacker signs it with a fake Microsoft Corporation certificate and calls svchost.exe.
Disabling of Windows Defender
Regardless of whether the cryptor or the miner was chosen, the downloader checks if one of the following AV processes is launched:
| 360DocProtect.exe | avgui.exe | dwservice.exe | McUICnt.exe |
| 360webshield.exe | avgwdsvc.exe | dwwatcher.exe | mcupdate.exe |
| AvastSvc.exe | Avira.OE.ServiceHost.exe | egui.exe | ProtectionUtilSurrogate.exe |
| AvastUI.exe | Avira.OE.Systray.exe | ekrn.exe | QHActiveDefense.exe |
| avgcsrva.exe | Avira.ServiceHost.exe | kav.exe | QHSafeTray.exe |
| avgemca.exe | Avira.Systray.exe | LUALL.exe | QHWatchdog.exe |
| avgidsagent.exe | avp.exe | LuComServer.exe | Rtvscan.exe |
| avgnsa.exe | ccApp.exe | McCSPServiceHost.exe | SMC.exe |
| avgnt.exe | ccSvcHst.exe | McPvTray.exe | SMCgui.exe |
| avgrsa.exe | Dumpuper.exe | McSACore.exe | spideragent.exe |
| avgrsx.exe | dwengine.exe | mcshield.exe | SymCorpUI.exe |
| avguard.exe | dwnetfilter.exe | McSvHost.exe |
If no AV process was found in the system, the Trojan will run several cmd commands that will disable Windows Defender in the system:
- cmd /C powershell Set-MpPreference -DisableRealtimeMonitoring $true
- cmd /C powershell Set-MpPreference -MAPSReporting 0
- cmd /C powershell Set-MpPreference -SubmitSamplesConsent 2
- taskkill /IM MSASCuiL.exe
- cmd /C REG ADD HKCU\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\Explorer /v HideSCAHealth /t REGDWORD /d 1 /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Explorer /v DisableNotificationCenter /t REGDWORD /d 1 /f
- cmd /C REG DELETE HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run /v SecurityHealth /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender /v DisableAntiSpyware /t REGDWORD /d 1 /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender /v AllowFastServiceStartup /t REGDWORD /d 0 /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender /v ServiceKeepAlive /t REGDWORD /d 0 /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection /v DisableIOAVProtection /t REGDWORD /d 1 /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Real-Time Protection /v DisableRealtimeMonitoring /t REGDWORD /d 1 /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Spynet /v DisableBlockAtFirstSeen /t REGDWORD /d 1 /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Spynet /v LocalSettingOverrideSpynetReporting /t REGDWORD /d 0 /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Spynet /v SubmitSamplesConsent /t REGDWORD /d 2 /f
- cmd /C REG ADD HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Defender\UX Configuration /v NotificationSuppress /t REGDWORD /d 1 /f
Sending the statistics
During their operation the downloader and cryptor modules send emails with statistics to a hardcoded address. These messages contain information about the current state of infection and other details such as:
- computer name;
- victim IP address;
- path of malware in the system;
- current date and time;
- malware build date.
The downloader sends the following states:
| Hello Install | Sent after the cryptor or miner is downloaded |
| Hello NTWRK | Sent after the downloader attempts to spread through the victim’s network |
| Error |
Sent if something goes wrong and contains the error code value |
The cryptor sends the following states:
| Locked | Shows that the cryptor was launched |
| Final | Shows that the cryptor has ended the encryption process |
Another interesting fact is that the downloader also has some spyware functionality – its messages include a list of running processes and an attachment with a screenshot.
Worm component
As one of its last actions the downloader tries to copy itself to all the computers in the local network. To do so, it calls the system command ‘net view /all’ which will return all the shares and then the Trojan creates the list.log file containing the names of computers with shared resources. For each computer listed in the file the Trojan checks if the folder Users is shared and, if so, the malware copies itself to the folder \AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Windows\Start Menu\Programs\Startup of each accessible user.
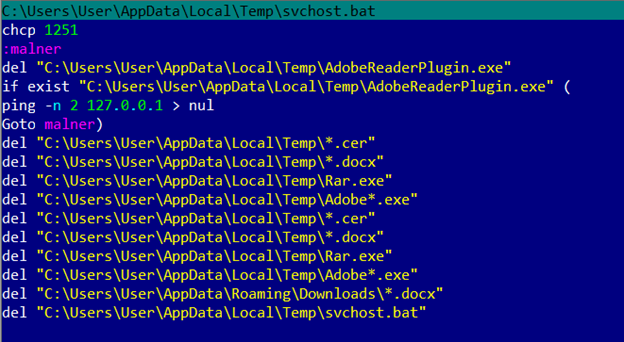
Self-deleting
Before shutting down the malware creates a batch file that deletes all ‘temporary’ files created during the infection process. This is a common practice for malware. The thing that interested us was the use of the Goto label ‘malner’. Perhaps this is a portmanteau of the words ‘malware’ and ‘miner’ used by the criminal.
Detection verdicts
Our products detect the malware described here with the following verdicts:
- Downloader: Trojan-Downloader.Win32.Rakhni.pwc
- Miner: not-a-virus:RiskTool.Win32.BitCoinMiner.iauu
- Cryptor: Trojan-Ransom.Win32.Rakhni.wbrf
In addition, all the malware samples are detected by the System Watcher component.
IoCs
Malicious document: 81C0DEDFA5CB858540D3DF459018172A
Downloader: F4EC1E3270D62DD4D542F286797877E3
Miner: BFF4503FF1650D8680F8E217E899C8F4
Cryptor: 96F460D5598269F45BCEAAED81F42E9B
URLs
hxxp://protnex[.]pw
hxxp://biserdio[.]pw

























To crypt, or to mine – that is the question