
Recently, news appeared about an interesting attack where cybercriminals infect iPhones and Mac OSX users with a rather peculiar malware dubbed WireLurker. You can find a thorough paper from Palo Alto here. First of all, it’s important to note that all Kaspersky Lab users are protected against this threat. The malicious files used by WireLurker are identified by our products with the following detection names:
- Mac OS X:
- Trojan-Downloader.OSX.WireLurker.a
- Trojan-Downloader.OSX.WireLurker.b
- Trojan.OSX.WireLurker.a
- Apple iOS:
- Trojan-Spy.IphoneOS.WireLurker.a
- Trojan-Spy.IphoneOS.WireLurker.b
- Windows:
- Trojan.Win32.Wirelurker.a
Our sensors observed connections to the malicious C&C server located in Hong Kong in July, 2014. These continued throughout the following months, although the volume remains low.
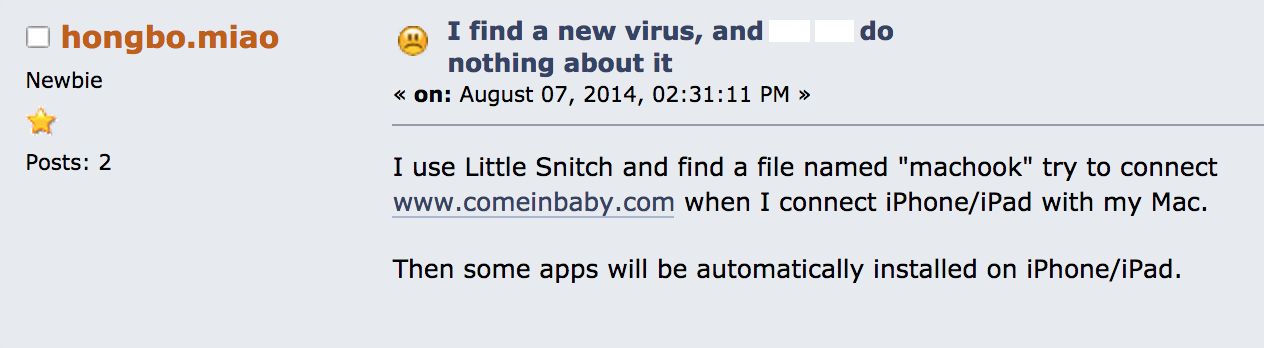
Interestingly, discussions on various online forums about this subject appeared earlier this year, notably in Chinese and Korean, but also on some English resources:
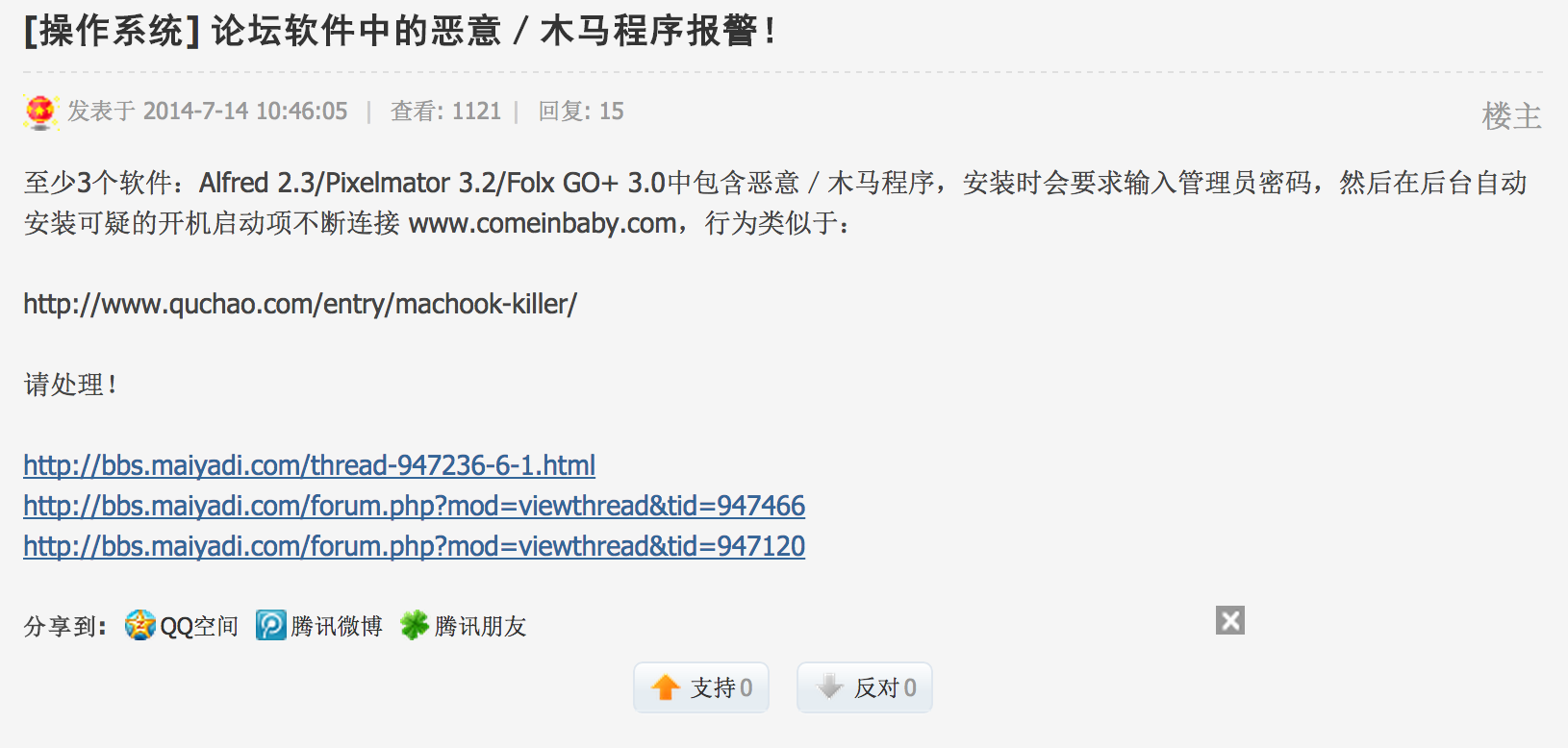
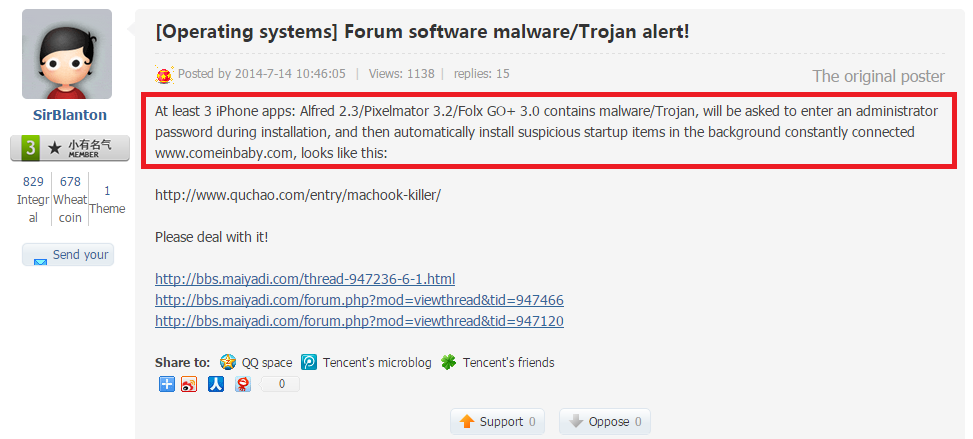
On July 14th, someone named SirBlanton complained about it on a Chinese speaking BBS:
Translation:
The discussion above happened on “bbs.maiyadi.com”, which is interesting, because another subdomain on “maiyadi.com” is used by the malware as a C&C (see below).
Even earlier, on May 29th, a discussion in Korea mentioned abnormal behavior of a Mac OS X infected by this threat:
Interestingly, Mac OS X and Apple iOS are not the only platforms through which these attacks were propagated. Yesterday, our friend Jaime Blasco from Alienvault discovered a Win32 malicious tool that appears to be related.
The WireLurker Windows module
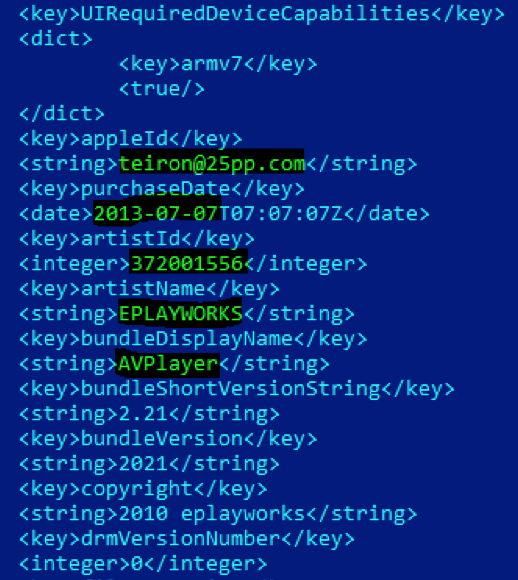
File name: 万能视频播放器 2.21.exe md5: fb4756b924c5943cdb73f5aec0cb7b14
Win32 WireLurker module
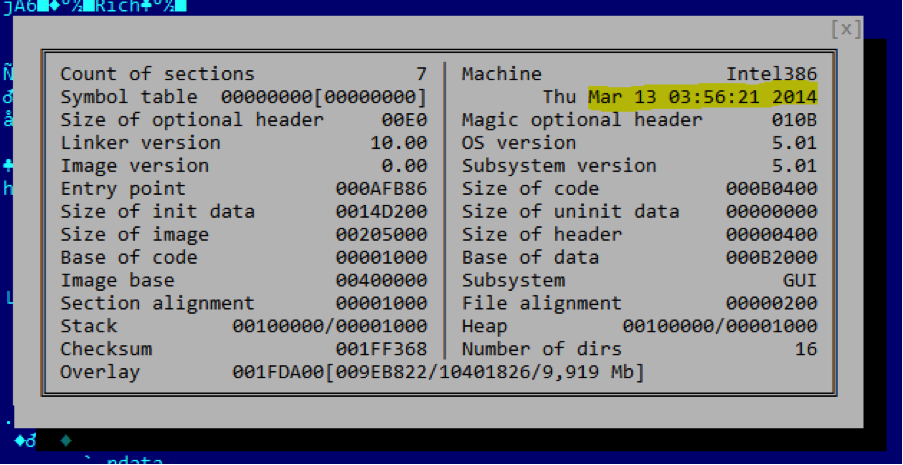
The file appears to have been compiled in March 2014, assuming the timestamp is not altered:
Full metadata set:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
Machine Type : Intel 386 or later, and compatibles Time Stamp : 2014:03:13 03:56:21-04:00 PE Type : PE32 Linker Version : 10.0 Code Size : 721920 Initialized Data Size : 1364480 Uninitialized Data Size : 0 Entry Point : 0xafb86 OS Version : 5.1 Image Version : 0.0 Subsystem Version : 5.1 Subsystem : Windows GUI File Version Number : 1.0.0.1 Product Version Number : 1.0.0.1 File Flags Mask : 0x003f File Flags : (none) File OS : Windows NT 32-bit Object File Type : Executable application File Subtype : 0 Language Code : Chinese (Simplified) Character Set : Unicode File Description : 绿色IPA安装器 File Version : 1.0.0.1 Internal Name : 绿色IPA安装器.exe Original Filename : 绿色IPA安装器.exe Product Name : 绿色IPA安装器 Product Version : 1.0.0.1 |
The internal file name is “绿色IPA安装器” which, when translated to English, means Green IPA installer. It supposed to be an application to install IPA files on iOS devices.
Interestingly, it contains a debug path which reveals information about the build:
E:lifeilibimobiledevice-win32-master_lastReleaseappinstaller.pdb
The application contains two IPA (Apple application archives) inside, one called “AVPlayer” and one called “apps”.
AVPlayer.app appears to be a legimitated iOS application that is used by the attackers as a decoy.
The image (icon) of the app can be seen below:
The “legit” application appears to have been authored by a popular developer going by the handle “teiron@25pp.com”.
The second IPA is more interesting. 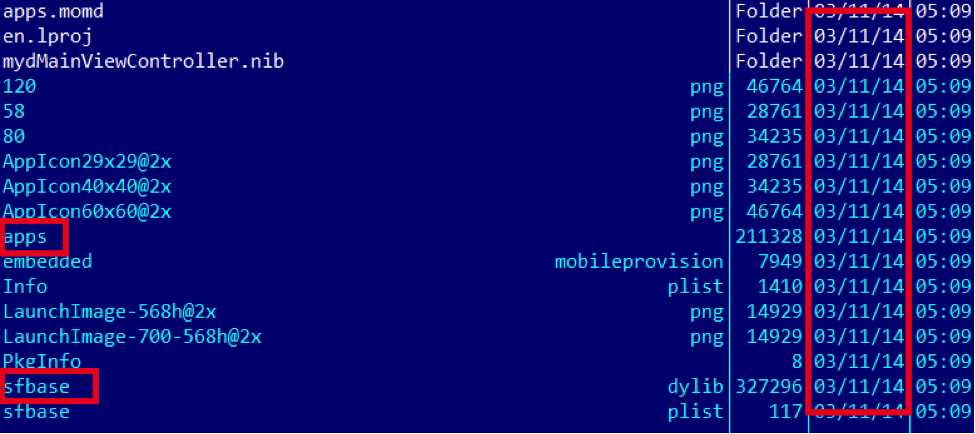 It appears to have been created in March 2014. “apps” communicates with the wellknown “comeinbaby[.]com”:
It appears to have been created in March 2014. “apps” communicates with the wellknown “comeinbaby[.]com”: 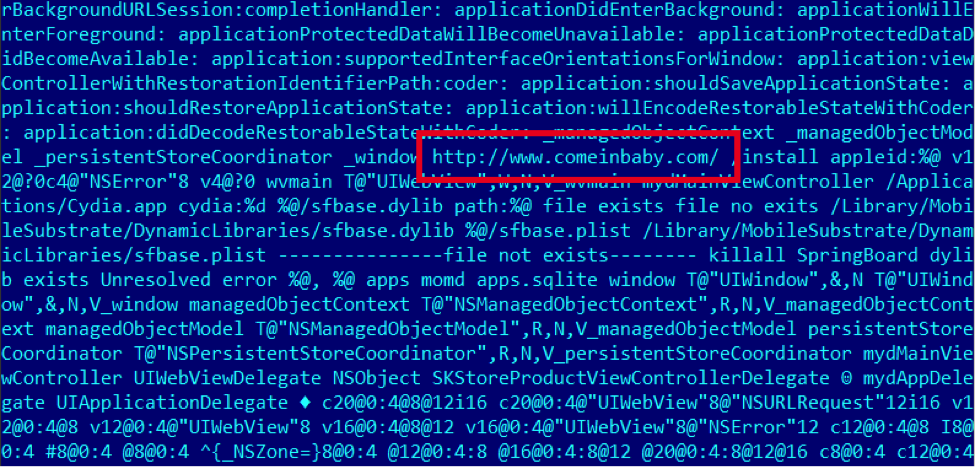 The sfbase.dylib part communicates with a different C&C:
The sfbase.dylib part communicates with a different C&C: 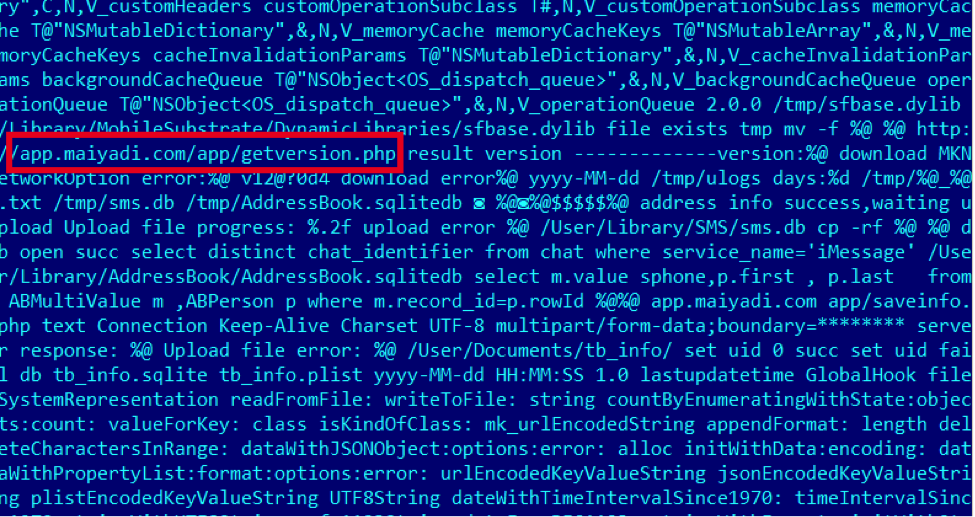 To summarize, the Win32 application described here allows the installation of the mentioned iOS payload to the victim’s iPhone. The creator likely developed it just to make sure Windows users can also get infected on their iOS devices.
To summarize, the Win32 application described here allows the installation of the mentioned iOS payload to the victim’s iPhone. The creator likely developed it just to make sure Windows users can also get infected on their iOS devices.
KSN Detections
Kaspersky Security Network (KSN) is a complex distributed infrastructure dedicated to processing cybersecurity-related data streams from millions of voluntary participants around the world. It delivers Kaspersky Lab’s security intelligence to every partner or customer who is connected to the Internet, ensuring the quickest reaction times, lowest false positive rate and maintaining the highest level of protection. A detailed description of KSN can be found here. The following chart below shows detections of WireLurker on OSX: 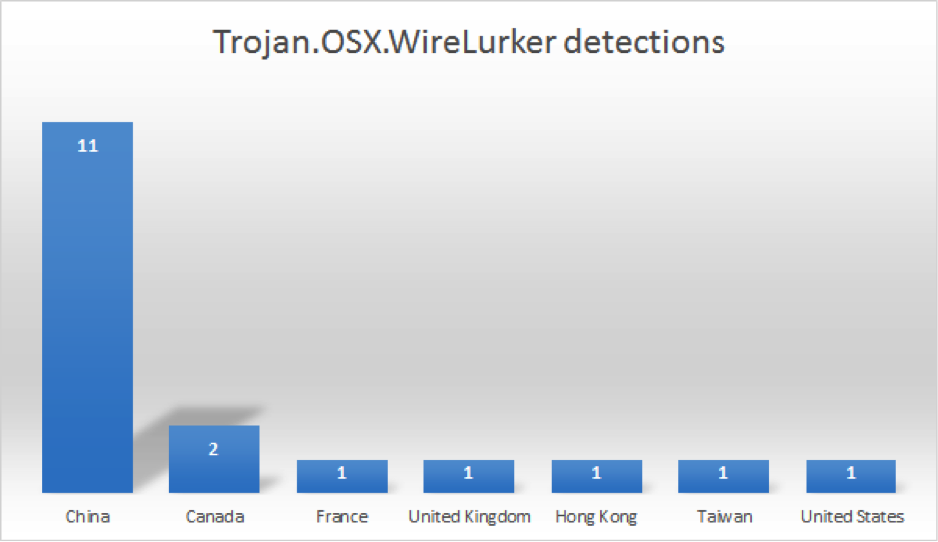
Over 60% of the detections are coming from China, which is to be expected.
Conclusions
This incident is yet another reminder of why the use of pirated software remains dangerous, no matter which platform you’re using. Downloading applications from unofficial sources, such as alternative marketplaces, file sharing websites or torrents and other P2P file sharing networks, increases the risk of malware infections. On Mac OS X for instance, it is one of the main infection vectors.
The need for anti-malware protection on Mac OS X devices cannot be overstated. It’s not only that your Mac OS X machine can get infected, but WireLurker showed us how the infection can move from your Mac to your iPhone. The good news is: there are plenty of options to chose from out there, including our own Kaspersky Internet Security for Mac.
As a first line of defense, Mac OS X users should check their Security & Privacy settings to make sure the configuration of their system is optimal. We recommend setting up Gatekeeper so that only applications downloaded from the Mac App Store and identified developers are allowed to be installed. More information on Gatekeeper can be found here.
Make sure to also check out our own guide for Mac security: 10 Simple Tips for Boosting The Security Of Your Mac
This should also be a wake-up call for Apple users and the way they think about security. Just like Mac OS X malware quickly evolved from being just a myth to becoming a sad reality, we are seeing iOS being targeted more and more often lately – with nobody being able to offer protection for this platform. Anti-malware vendors are still not allowed to develop protection for iPhone users.
In the light of recent events, will this strategy change in the future?
Indicators of compromise:
C&Cs:
app.maiyadi[.]com
comeinbaby[.]com
61.147.80.73
124.248.245.78
MD5s:
3fa4e5fec53dfc9fc88ced651aa858c6
5b43df4fac4cac52412126a6c604853c
88025c70d8d9cd14c00a66d3f3e07a84
9037cf29ed485dae11e22955724a00e7
a3ce6c8166eec5ae8ea059a7d49b5669
aa6fe189baa355a65e6aafac1e765f41
bc3aa0142fb15ea65de7833d65a70e36
c4264b9607a68de8b9bbbe30436f5f28
c6d95a37ba39c0fa6688d12b4260ee7d
c9841e34da270d94b35ae3f724160d5e
dca13b4ff64bcd6876c13bbb4a22f450
e03402006332a6e17c36e569178d2097
fb4756b924c5943cdb73f5aec0cb7b14
iOS trojan WireLurker: statistics and new information






















Erwin Geirnaert
Hi,
Interesting post. We blogged in May 2014 on something related: an iPad that allowed a remote user to take control of the screen. See https://www.zionsecurity.com/blog/2014/5/ipad-air-spyware-help-needed-security-community
Would installing Kaspersky on the iPad reveal traces of the malware?
Best regards,
Erwin