
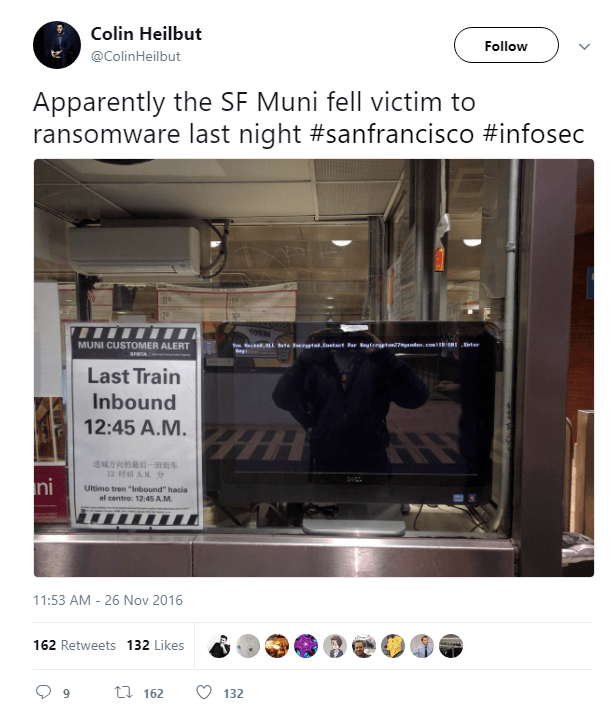
At the end of 2016, there was a major attack against San Francisco’s Municipal Transportation Agency. The attack was done using Mamba ransomware. This ransomware uses a legitimate utility called DiskCryptor for full disk encryption. This month, we noted that the group behind this ransomware has resumed their attacks against corporations.
Attack Geography
We are currently observing attacks against corporations that are located in:
- Brazil
- Saudi Arabia
Attack Vector
As usual, this group gains access to an organization’s network and uses the psexec utility to execute the ransomware. Also, it is important to mention that for each machine in the victim’s network, the threat executor generates a password for the DiskCryptor utility. This password is passed via command line arguments to the ransomware dropper.
Technical Analysis
In a nutshell, the malicious activity can be separated into two stages:
Stage 1 (Preparation):
- Create folder “C:\xampp\http“
- Drop DiskCryptor components into the folder
- Install DiskCryptor driver
- Register system service called DefragmentService
- Reboot victim machine
Stage 2 (Encryption):
- Setup bootloader to MBR and encrypt disk partitions using DiskCryptor software
- Clean up
- Reboot victim machine
Stage 1 (Preparation)
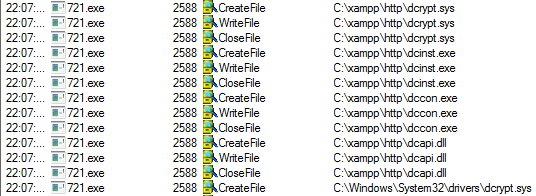
As the trojan uses the DiskCryptor utility, the first stage deals with installing this tool on a victim machine. The malicious dropper stores DiskCryptor’s modules in their own resources.
Depending on OS information, the malware is able to choose between 32- or 64-bit DiskCryptor modules. The necessary modules will be dropped into the “C:\xampp\http” folder.
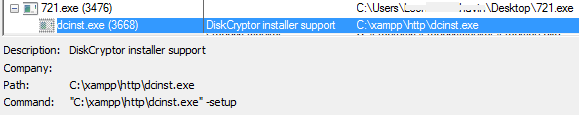
After that, it launches the dropped DiskCryptor installer.
When DiskCryptor is installed, the malware creates a service that has SERVICE_ALL_ACCESS and SERVICE_AUTO_START parameters.
The last step of Stage 1 is to reboot the system.
Stage 2 (Encryption)
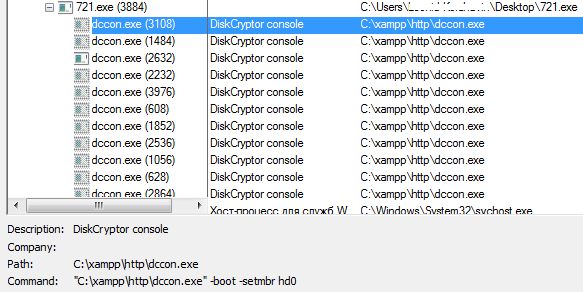
Using the DiskCryptor software, the malware sets up a new bootloader to MBR.
The bootloader contains the ransom message for the victim.
After the bootloader is set, disk partitions would be encrypted using a password, previously specified as a command line argument for the dropper.
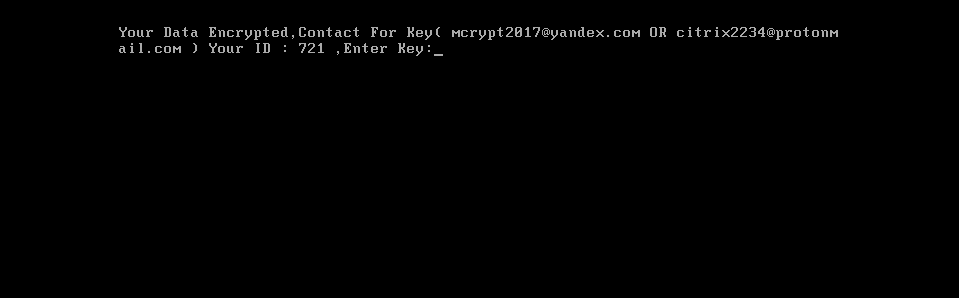
When the encryption ends, the system will be rebooted, and a victim will see a ransom note on the screen.
Kaspersky Lab products detect this threat with the help of the System Watcher component with the following verdict: PDM:Trojan.Win32.Generic.
Decryption
Unfortunately, there is no way to decrypt data that has been encrypted using the DiskCryptor utility because this legitimate utility uses strong encryption algorithms.
IOCs:
79ED93DF3BEC7CD95CE60E6EE35F46A1
The return of Mamba ransomware

























someguy
What disassembler and hex editor do you guys use?
otherguy
Looks like Hiew and IDA Pro.
Tomáš
IDA Pro is mostly used
iamnoob
based from the pic. Disassembler: IDA PRO and Hex View/Editor: HIEW
nilesh
look like idapro
Simon
Possible to bruteforce password?