
Statistics across all threats
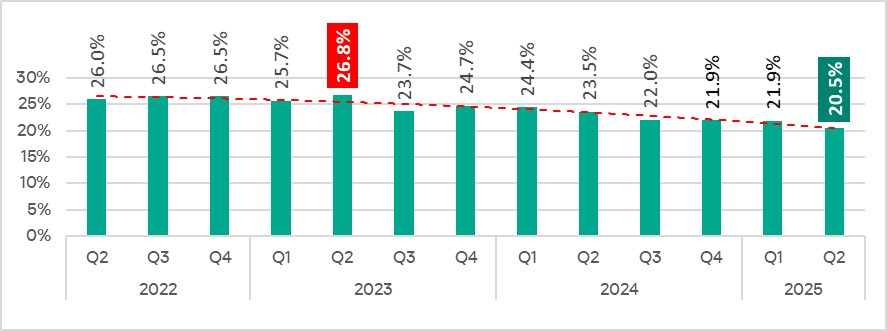
In Q2 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked decreased by 1.4 pp from the previous quarter to 20.5%.
Compared to Q2 2024, the rate decreased by 3.0 pp.
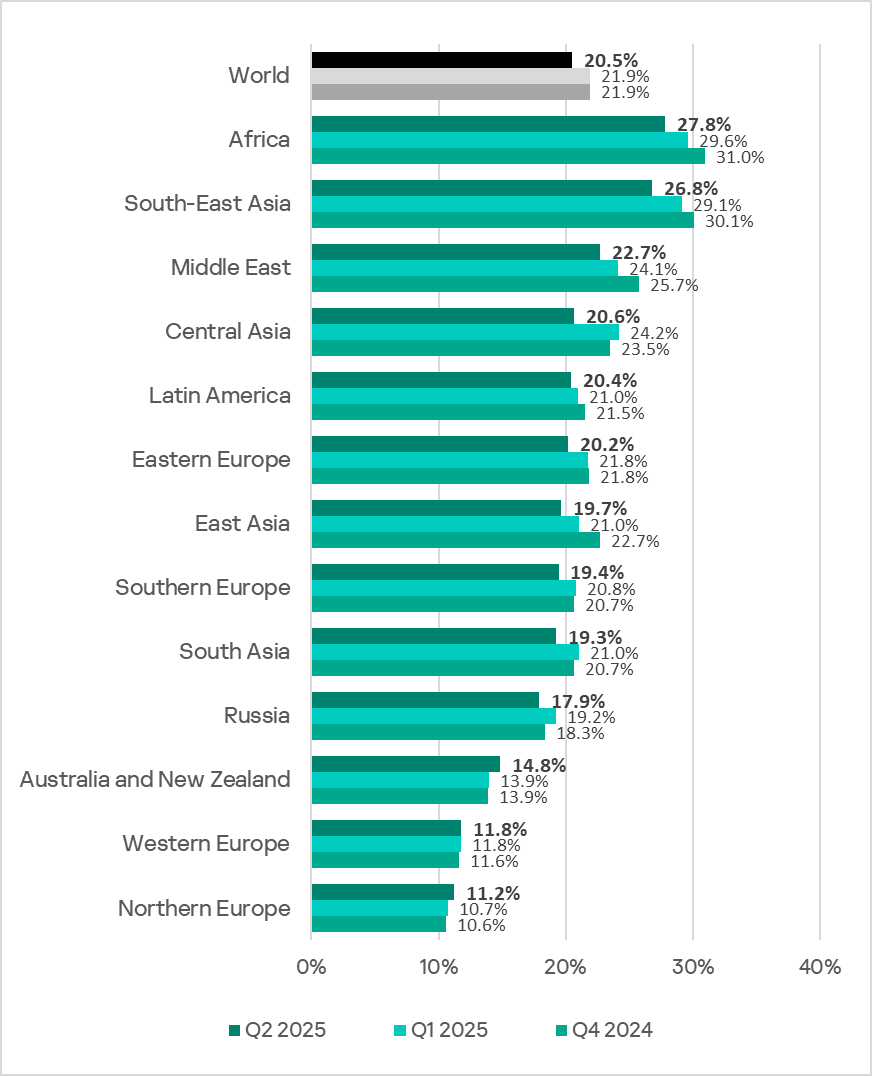
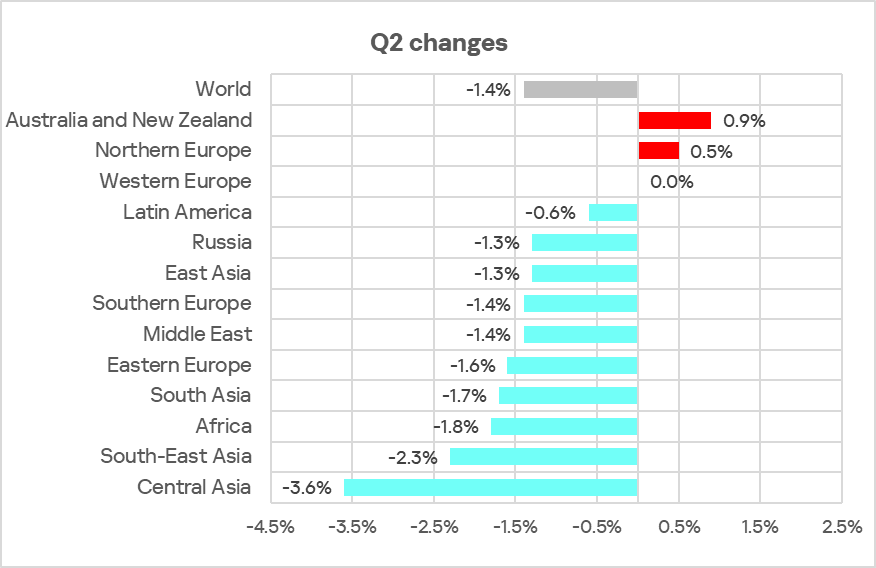
Regionally, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked ranged from 11.2% in Northern Europe to 27.8% in Africa.
In most of the regions surveyed in this report, the figures decreased from the previous quarter. They increased only in Australia and New Zealand, as well as Northern Europe.
Selected industries
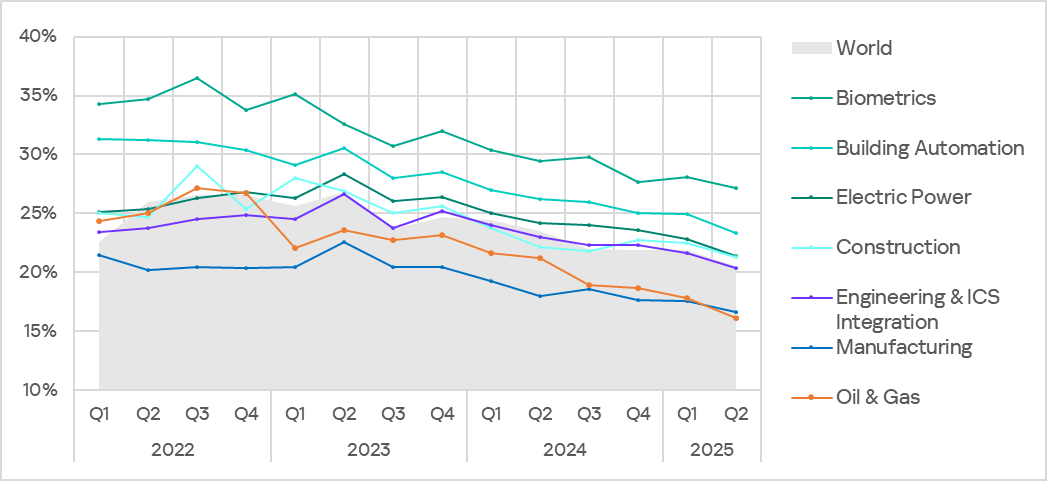
The biometrics sector led the ranking of the industries and OT infrastructures surveyed in this report in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
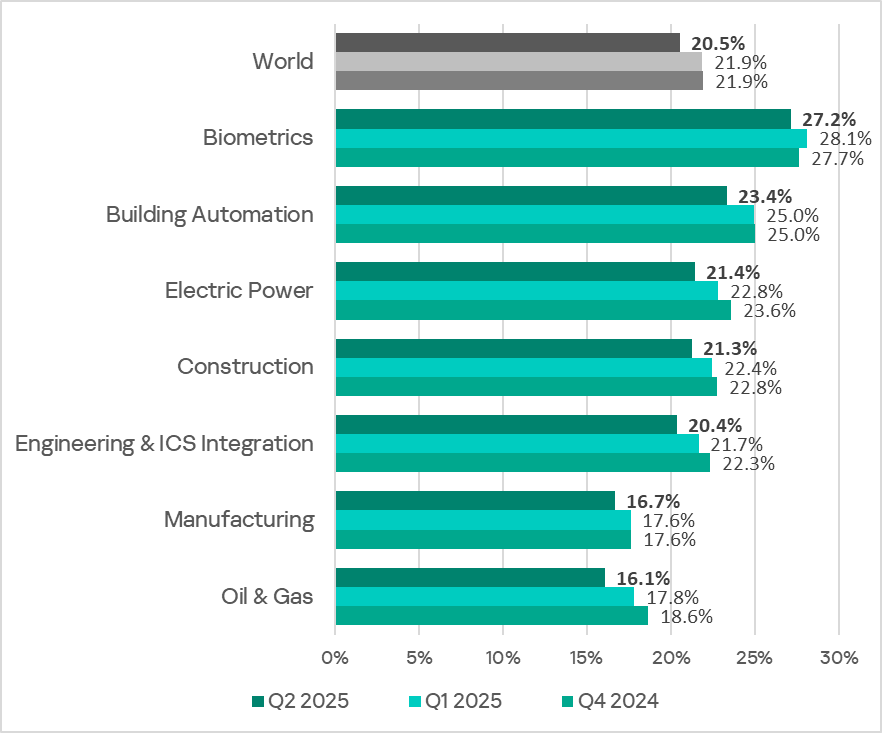
Ranking of industries and OT infrastructures by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked
In Q2 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked decreased across all industries.
Diversity of detected malicious objects
In Q2 2025, Kaspersky security solutions blocked malware from 10,408 different malware families from various categories on industrial automation systems.
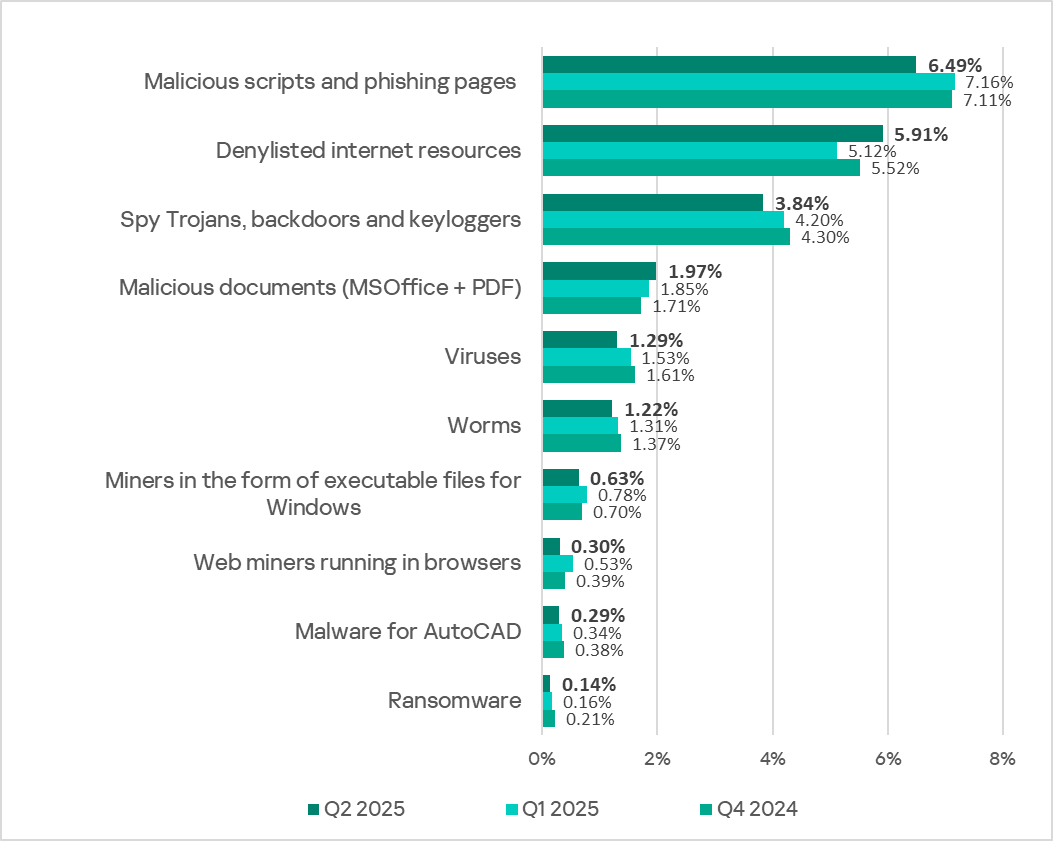
Percentage of ICS computers on which the activity of malicious objects from various categories was blocked
The only increases were in the percentages of ICS computers on which denylisted internet resources (1.2 times more than in the previous quarter) and malicious documents (1.1 times more) were blocked.
Main threat sources
Depending on the threat detection and blocking scenario, it is not always possible to reliably identify the source. The circumstantial evidence for a specific source can be the blocked threat’s type (category).
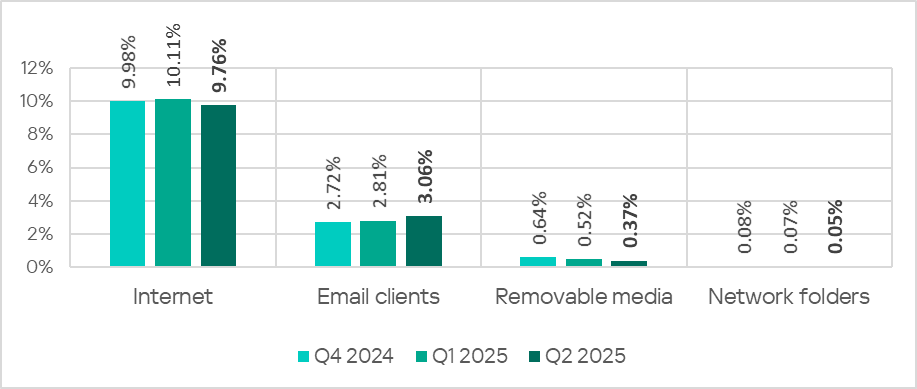
The internet (visiting malicious or compromised internet resources; malicious content distributed via messengers; cloud data storage and processing services and CDNs), email clients (phishing emails), and removable storage devices remain the primary sources of threats to computers in an organization’s technology infrastructure.
In Q2 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which threats from email clients were blocked continued to increase. The main categories of threats from email clients blocked on ICS computers are malicious documents, spyware, malicious scripts and phishing pages. The indicator increased in all regions except Russia. By contrast, the global average for other threat sources decreased. Moreover, the rates reached their lowest levels since Q2 2022.
The same computer can be attacked by several categories of malware from the same source during a quarter. That computer is counted when calculating the percentage of attacked computers for each threat category, but is only counted once for the threat source (we count unique attacked computers). In addition, it is not always possible to accurately determine the initial infection attempt. Therefore, the total percentage of ICS computers on which various categories of threats from a certain source were blocked exceeds the percentage of threats from the source itself.
The rates for all threat sources varied across the monitored regions.
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from the internet were blocked ranged from 6.35% in East Asia to 11.88% in Africa
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from email clients were blocked ranged from 0.80% in Russia to 7.23% in Southern Europe
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from removable media were blocked ranged from 0.04% in Australia and New Zealand to 1.77% in Africa
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from network folders were blocked ranged from 0.01% in Northern Europe to 0.25% in East Asia
Threat categories
A typical attack blocked within an OT network is a multi-stage process, where each subsequent step by the attackers is aimed at increasing privileges and gaining access to other systems by exploiting the security problems of industrial enterprises, including technological infrastructures.
It is worth noting that during the attack, intruders often repeat the same steps (TTPs), especially when they use malicious scripts and established communication channels with the management and control infrastructure (C2) to move laterally within the network and advance the attack.
Malicious objects used for initial infection
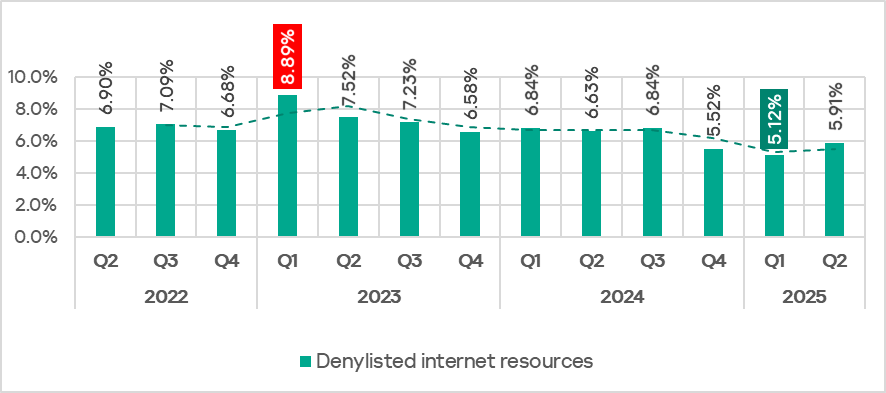
In Q2 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which denylisted internet resources were blocked increased to 5.91%.
The percentage of ICS computers on which denylisted internet resources were blocked ranged from 3.28% in East Asia to 6.98% in Africa. Russia and Eastern Europe were also among the top three regions for this indicator. It increased in all regions and this growth is associated with the addition of direct links to malicious code hosted on popular public websites and file-sharing services.
The percentage of ICS computers on which malicious documents were blocked has grown for two consecutive quarters. The rate reached 1.97% (up 0.12 pp) and returned to the level seen in Q3 2024. The percentage increased in all regions except Latin America.
The percentage of ICS computers on which malicious scripts and phishing pages were blocked decreased to 6.49% (down 0.67 pp).
Next-stage malware
Malicious objects used to initially infect computers deliver next-stage malware (spyware, ransomware, and miners) to victims’ computers. As a rule, the higher the percentage of ICS computers on which the initial infection malware is blocked, the higher the percentage for next-stage malware.
In Q2 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects from all categories were blocked decreased. The rates are:
- Spyware: 3.84% (down 0.36 pp);
- Ransomware: 0.14% (down 0.02 pp);
- Miners in the form of executable files for Windows: 0.63% (down 0.15 pp);
- Web miners: 0.30% (down 0.23 pp), its lowest level since Q2 2022.
Self-propagating malware
Self-propagating malware (worms and viruses) is a category unto itself. Worms and virus-infected files were originally used for initial infection, but as botnet functionality evolved, they took on next-stage characteristics.
To spread across ICS networks, viruses and worms rely on removable media, network folders, infected files including backups, and network attacks on outdated software such as Radmin2.
In Q2 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which worms and viruses were blocked decreased to 1.22% (down 0.09 pp) and 1.29% (down 0.24 pp). Both are the lowest values since Q2 2022.
AutoCAD malware
This category of malware can spread in a variety of ways, so it does not belong to a specific group.
In Q2 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which AutoCAD malware was blocked continued to decrease to 0.29% (down 0.05 pp) and reached its lowest level since Q2 2022.
For more information on industrial threats see the full version of the report.















Threat landscape for industrial automation systems in Q2 2025