
Trends
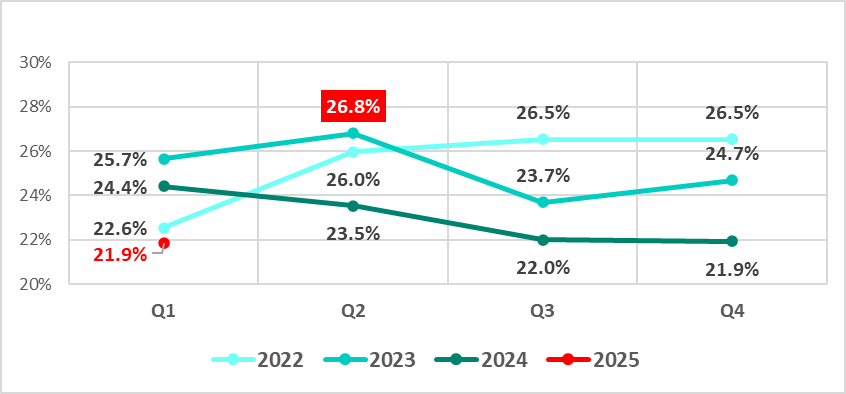
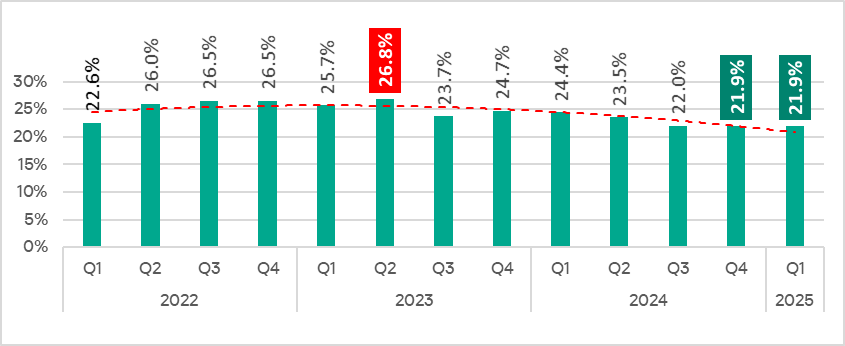
Relative stability from quarter to quarter. The percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked remained unchanged from Q4 2024 at 21.9%. Over the last three quarters, the value has ranged from 22.0% to 21.9%.
The quarterly figures are decreasing from year to year. Since Q2 2023, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked has been lower than the indicator of the same quarter of the previous year. Compared to Q1 2024, the figure decreased by 2.5 pp.
In January–March 2025, the figures were the lowest compared to the same months of the previous four years.
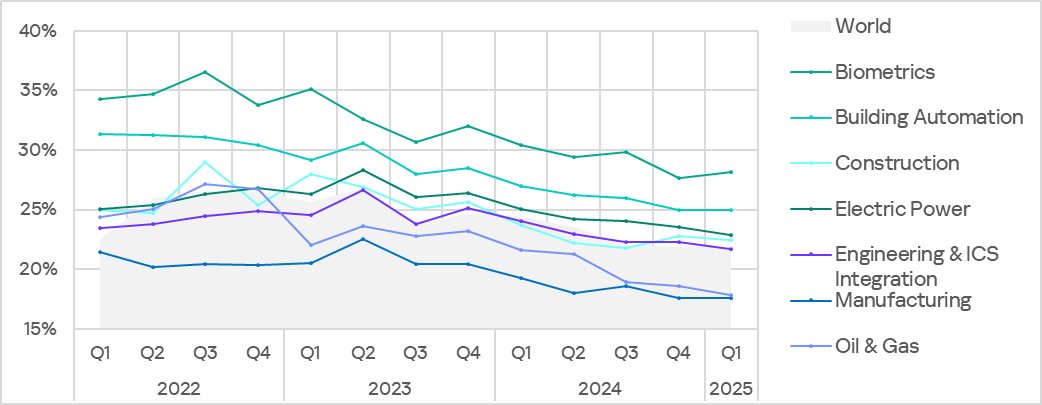
The biometrics sector continues to lead the selected industries / OT infrastructure types. This is the only OT infrastructure type where the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked increased during the quarter.
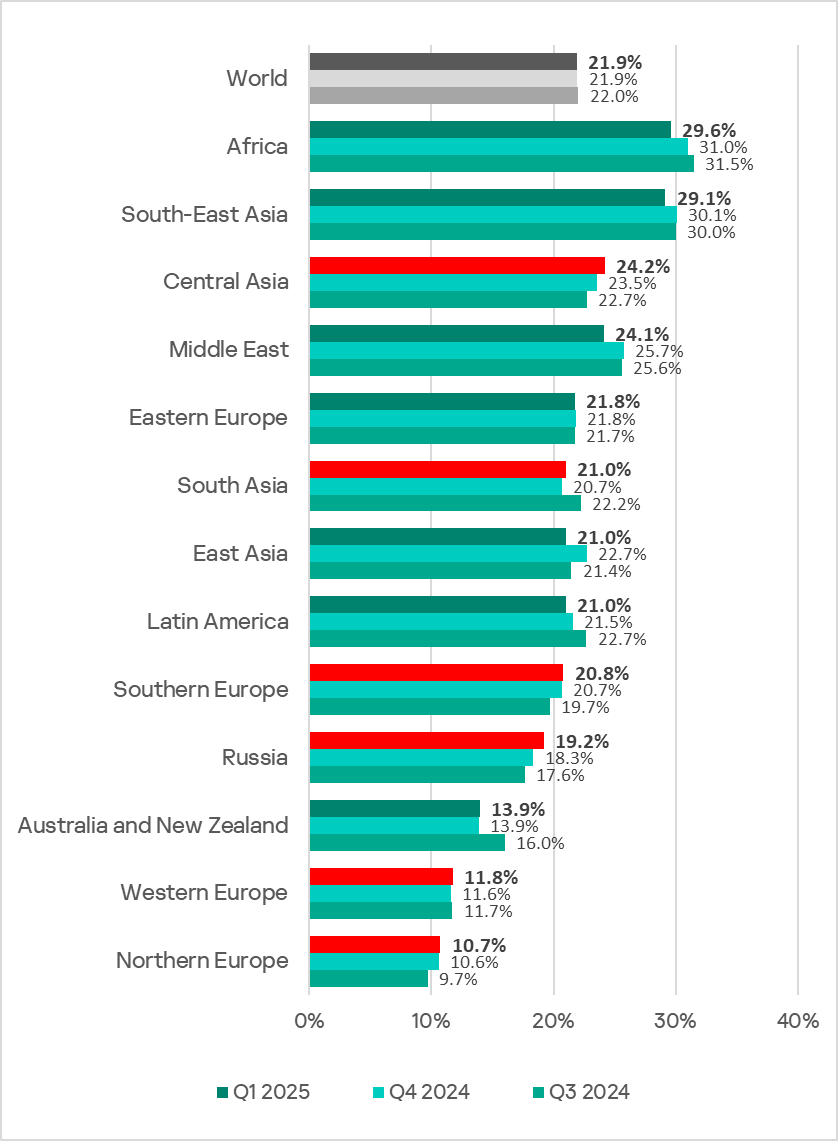
Threat levels in different regions still vary. In Q1 2025, the percentage of affected ICS computers ranged from 10.7% in Northern Europe to 29.6% in Africa. In eight out of 13 regions, the figures ranged from 19.0% to 25.0%.
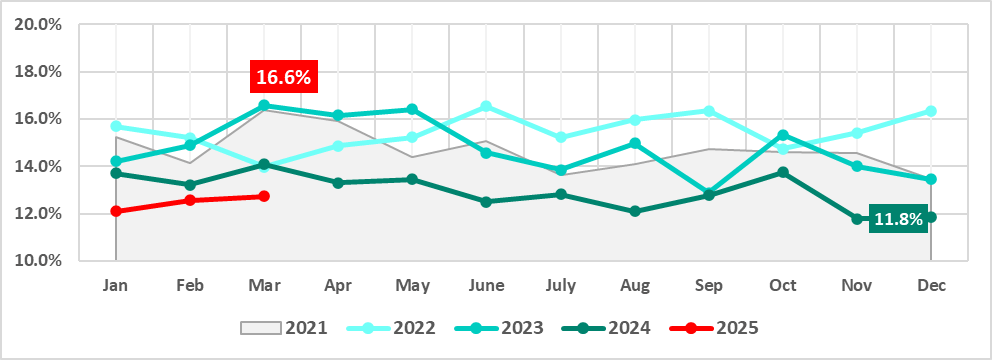
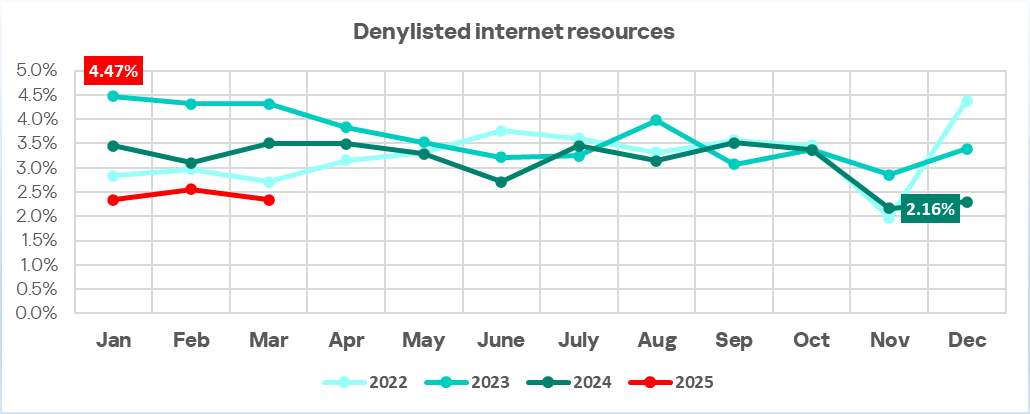
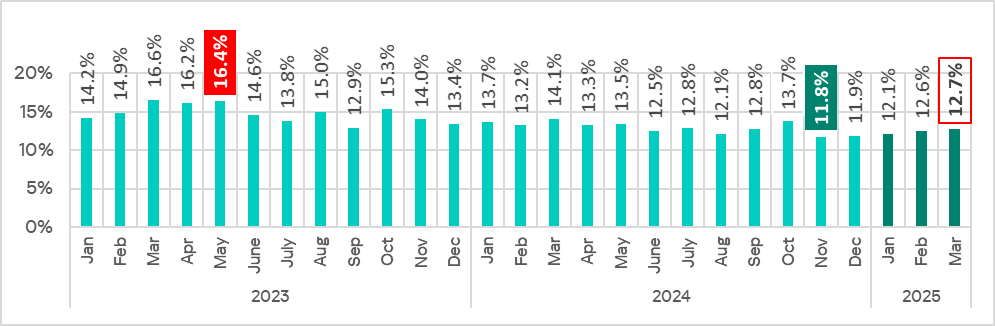
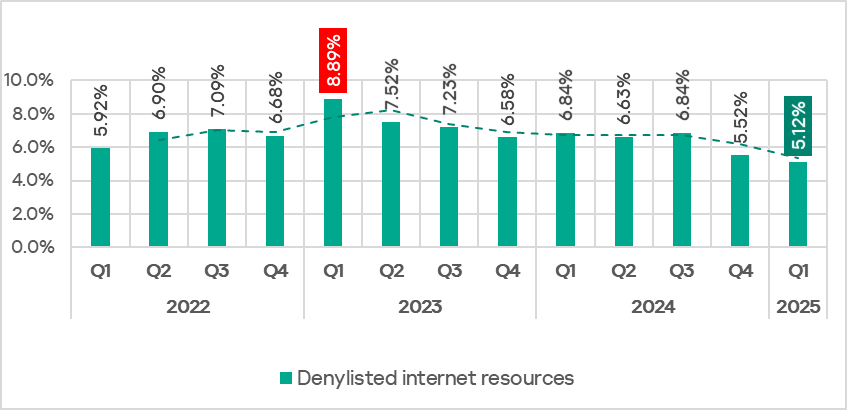
The percentage of ICS computers on which denylisted internet resources were blocked continues to decrease. It reached its lowest level since the beginning of 2022. In the first three months of 2025, the corresponding figures were lower than those in January–March of the previous three years.
Changes in the percentage of ICS computers on which initial-infection malware was blocked lead to changes in the percentage of next-stage malware. In Q1 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which various types of malware spread via the internet and email were blocked increased for the first time since the beginning of 2023.
The internet is the primary source of threats to ICS computers. The main categories of threats from the internet are denylisted internet resources, malicious scripts and phishing pages.
The main categories of threats spreading via email are malicious documents, spyware, malicious scripts and phishing pages.
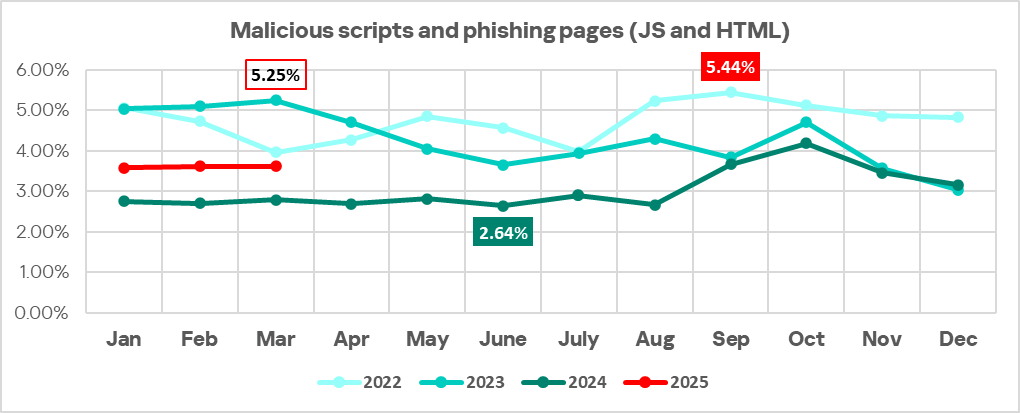
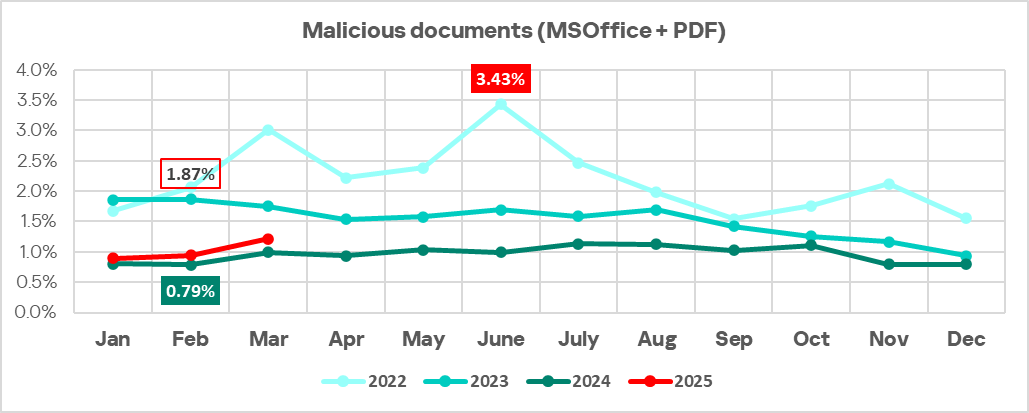
The percentage of ICS computers on which malicious scripts and phishing pages, and malicious documents were blocked increased in Q1 2025. In January–March, the monthly values in these two categories of threats were higher than in the same months of 2024.
The leading category of malware used for initial infection of ICS computers (see below) is malicious scripts and phishing pages.
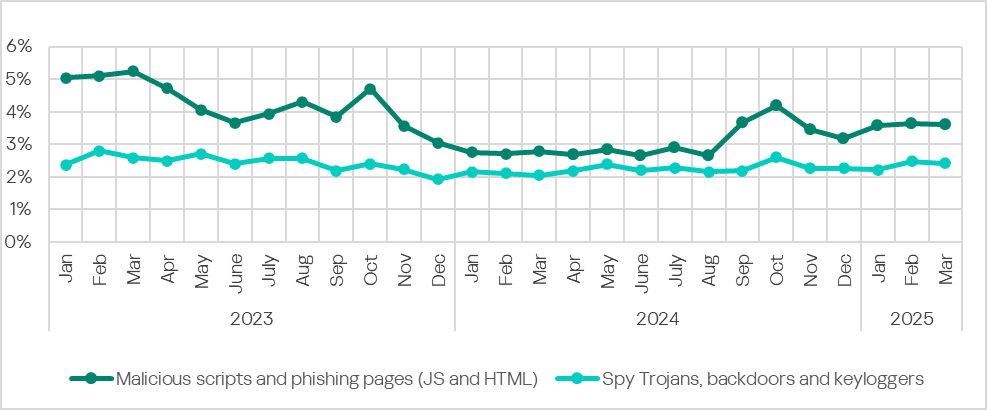
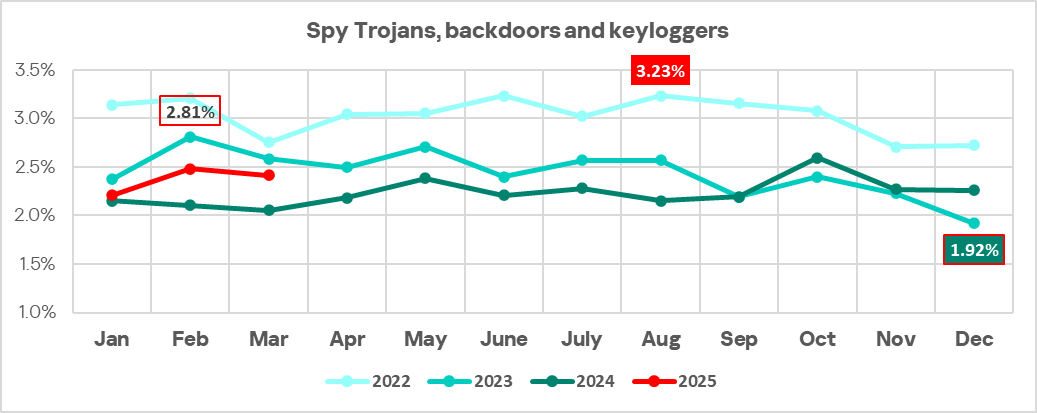
Most malicious scripts and phishing pages act as droppers or loaders of next-stage malware (spyware, crypto miners and ransomware). The strong correlation between the values for malicious scripts and phishing pages, and spyware is clearly visible in the graph below.
Similar to malicious scripts and phishing pages, the percentage of ICS computers on which spyware was blocked was higher in the first three months of 2025 than in the same months of 2024.
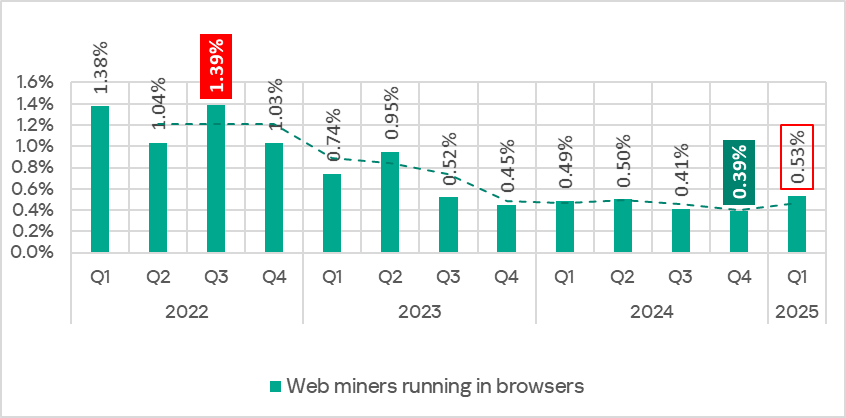
The percentage of ICS computers on which miners (web miners and miners in the form of executable files for Windows) were blocked in Q1 2025 also increased.
Statistics across all threats
In Q1 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked remained at the same level as in the previous quarter: 21.9%.
Compared to Q1 2024, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked decreased by 2.5 pp. However, it increased from January to March of 2025 when it reached its highest value in the quarter.
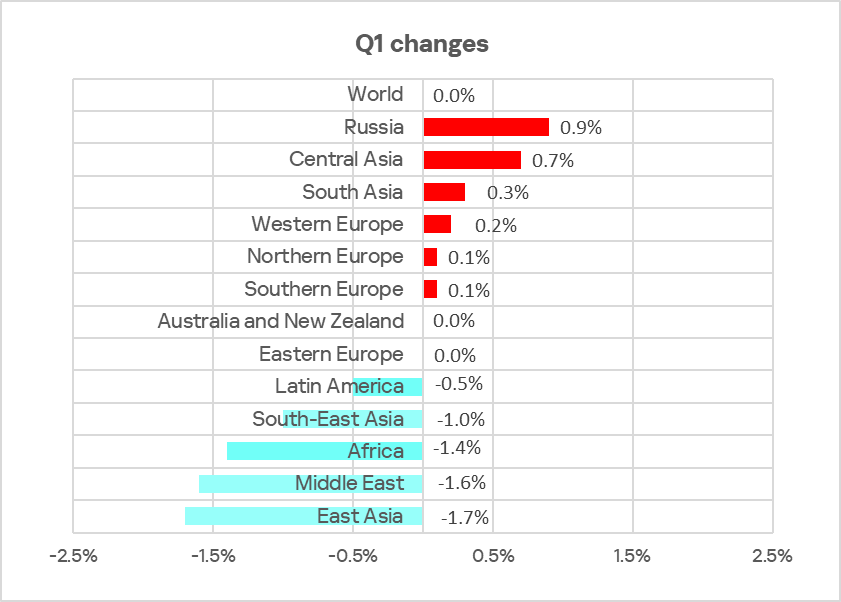
Regionally, the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked ranged from 10.7% in Northern Europe to 29.6% in Africa.
In six of the 13 regions surveyed in this report, the figures increased from the previous quarter, with the largest change occurring in Russia.
Selected industries
The biometrics sector led the ranking of the industries and OT infrastructures surveyed in this report in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked.
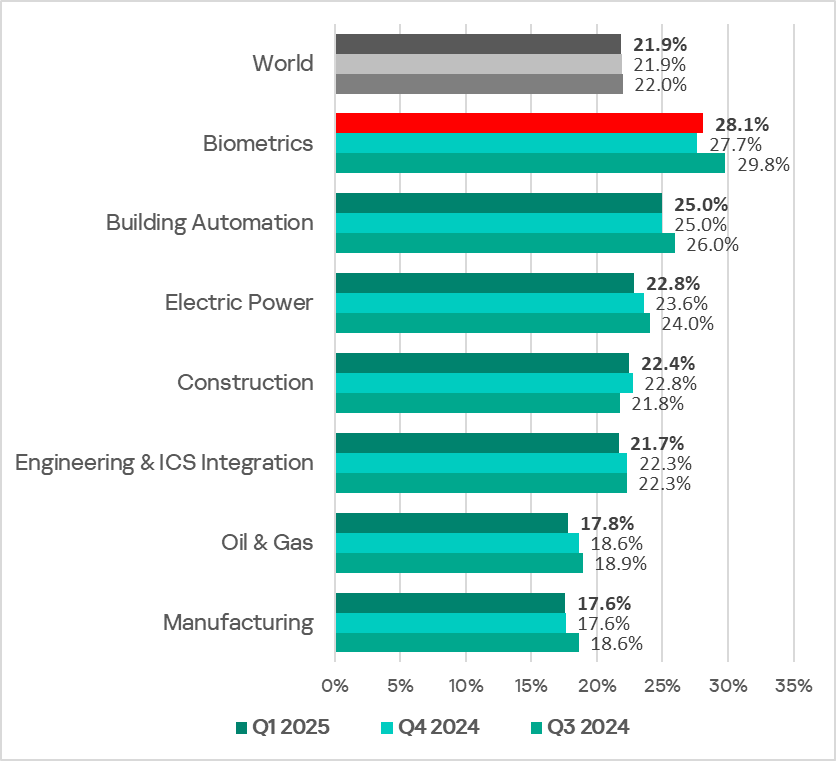
Ranking of industries and OT infrastructures by percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked, Q1 2025
The biometrics sector was also the only OT infrastructure type where the percentage of ICS computers on which malicious objects were blocked increased slightly. Despite this, the long-term trend is clearly downward.
Diversity of detected malicious objects
In Q1 2025, Kaspersky security solutions blocked malware from 11,679 different malware families in various categories on industrial automation systems.
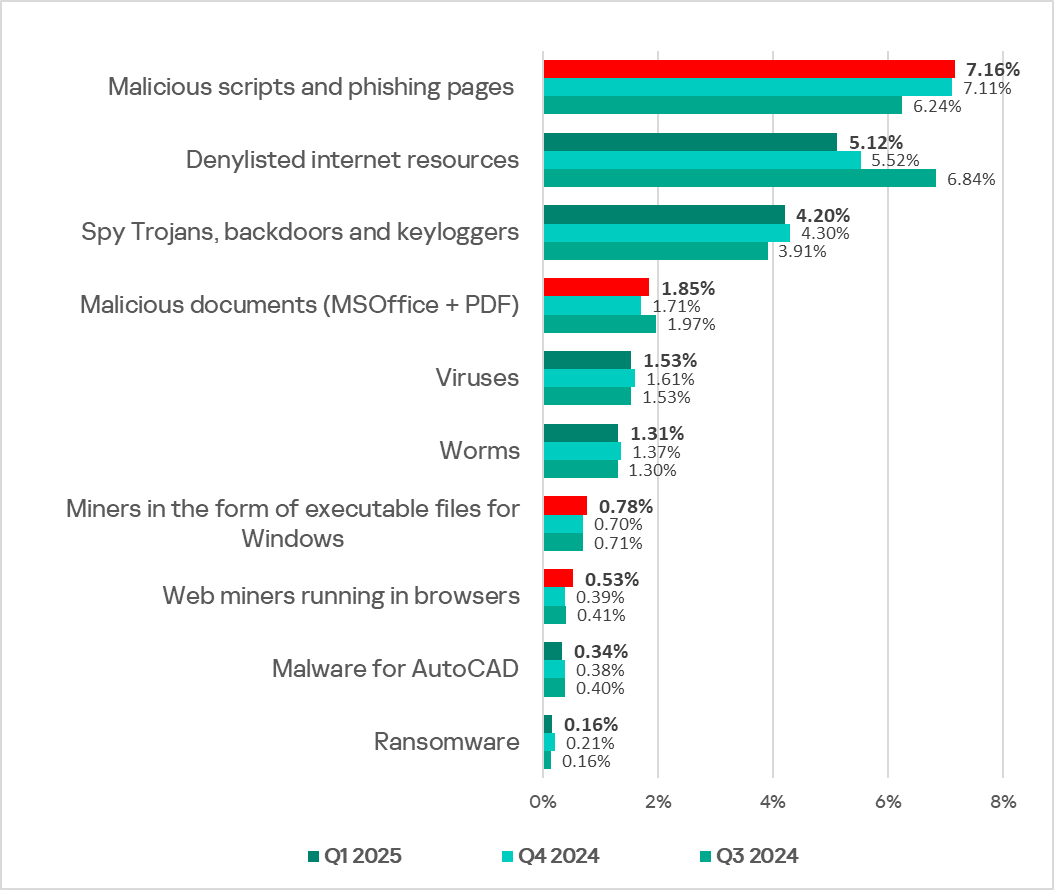
Percentage of ICS computers on which the activity of malicious objects from various categories was blocked
The largest proportional increase in Q1 2025 was in the percentage of ICS computers on which web miners (1.4 times more than in the previous quarter) and malicious documents (1.1 times more) were blocked.
Main threat sources
Depending on the threat detection and blocking scenario, it is not always possible to reliably identify the source. The circumstantial evidence for a specific source can be the blocked threat’s type (category).
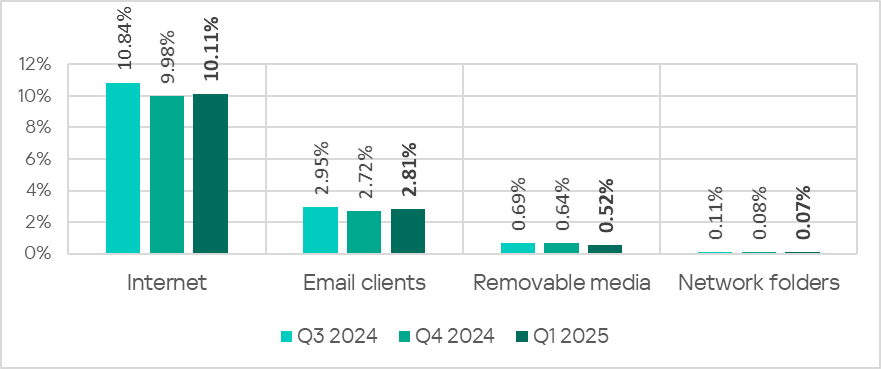
The internet (visiting malicious or compromised internet resources; malicious content distributed via messengers; cloud data storage and processing services and CDNs), email clients (phishing emails), and removable storage devices remain the primary sources of threats to computers in an organization’s OT infrastructure.
In Q1 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which threats from the internet and email clients were blocked increased for the first time since the end of 2023.
The rates for all threat sources varied across the monitored regions.
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from the internet were blocked ranged from 5.2% in Northern Europe to 12.8% in Africa.
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from email clients were blocked ranged from 0.88% in Russia to 6.8% in Southern Europe.
- The percentage of ICS computers on which threats from removable media were blocked ranged from 0.06% in Australia and New Zealand to 2.4% in Africa.
Threat categories
Typical attacks blocked within an OT network are a multi-stage process, where each subsequent step by the attackers is aimed at increasing privileges and gaining access to other systems by exploiting security flaws in industrial enterprises, including OT infrastructures.
It is worth noting that during the attack, intruders often repeat the same steps (TTP), especially when they use malicious scripts and established communication channels with the management and control infrastructure (C2) to move laterally within the network and advance the attack.
Malicious objects used for initial infection
In Q1 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which denylisted internet resources were blocked decreased to its lowest value since the beginning of 2022.
The decline in the percentage of denylisted internet resources since November 2024 was likely influenced not only by proactive threat mitigation at various levels, but also by techniques used by attackers to circumvent the blocking mechanisms based on the resource’s reputation, thus redistributing the protection burden to other detection technologies.
A detected malicious web resource may not always be added to a denylist because attackers are increasingly using legitimate internet resources and services such as content delivery network (CDN) platforms, messengers, and cloud storage. These services allow malicious code to be distributed through unique links to unique content, making it difficult to use reputation-based blocking tactics. We strongly recommend that industrial organizations implement policy-based blocking of such services, at least for OT networks where the need for such services is extremely rare for objective reasons.
The percentage of ICS computers on which malicious documents as well as malicious scripts and phishing pages were blocked increased slightly, to 1.85% (by 0.14 pp) and 7.16% (by 0.05 pp) respectively.
Next-stage malware
Malicious objects used to initially infect computers deliver next-stage malware – spyware, ransomware, and miners – to victims’ computers. As a rule, the higher the percentage of ICS computers on which the initial infection malware is blocked, the higher the percentage for next-stage malware.
In Q1 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which spyware and ransomware were blocked decreased, reaching 4.20% (by losing 0.1 pp) and 0.16% (by losing 0.05 pp) respectively. Conversely, the indicator for miners increased. The percentage of ICS computers on which miners in the form of executable files for Windows and web miners were blocked increased to 0.78% (by 0.08 pp) and 0.53% (by 0.14 pp), respectively. The latter indicator reached its highest value since Q3 2023.
Self-propagating malware
Self-propagating malware (worms and viruses) is a category unto itself. Worms and virus-infected files were originally used for initial infection, but as botnet functionality evolved, they took on next-stage characteristics.
To spread across ICS networks, viruses and worms rely on removable media, network folders, infected files including backups, and network attacks on outdated software, such as Radmin2.
In Q1 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which worms and viruses were blocked decreased to 1.31% (by losing 0.06 pp) and 1.53% (by losing 0.08 pp), respectively.
AutoCAD malware
AutoCAD malware is typically a low-level threat, coming last in the malware category rankings in terms of the percentage of ICS computers on which it was blocked.
In Q1 2025, the percentage of ICS computers on which AutoCAD malware was blocked continued to decrease (by losing 0.04 pp) and reached 0.034%.
You can find more information on industrial threats in the full version of the report.















Threat landscape for industrial automation systems in Q1 2025